Why Pea Peptides Are Redefining Plant-Based Performance Nutrition
As the demand for plant-based, clean-label, and performance-oriented nutrition intensifies, pea peptide has emerged as a leading candidate for brands seeking both efficacy and sustainability. In functional foods, dietary supplements, and active nutrition products, pea-derived peptides offer a powerful combination of bioactivity, digestibility, and eco-conscious appeal.
This article explores the science, applications, and commercial strategies surrounding pea peptides—highlighting why this ingredient should be a cornerstone in your next-generation muscle or weight management formulation.
What Are Pea Peptides?
Pea peptides are short-chain amino acid sequences produced through the enzymatic hydrolysis of high-quality pea protein. Unlike intact pea protein isolates or concentrates, peptides are smaller in size and more rapidly absorbed by the body, often resulting in improved functional properties such as enhanced bioavailability and faster physiological effects [1].
Pea peptide production typically involves a precision enzymatic process followed by membrane filtration, yielding highly purified peptides with customizable molecular weight distributions. This makes them suitable for a variety of targeted nutritional applications—from high-performance sports drinks to satiety-enhancing snacks.
Why Pea Peptides Are Gaining Global Traction
● Plant-Based and Clean-Label Appeal
In a market driven by health-conscious and environmentally aware consumers, the shift from animal-based to plant-based proteins is accelerating. Pea peptides are naturally vegan, gluten-free, non-GMO, and hypoallergenic—meeting the clean-label criteria of modern functional nutrition products [2].
● Superior Digestibility and Bioactivity
Thanks to their hydrolyzed structure, pea peptides are more readily absorbed than intact proteins. Research shows that pea peptides can stimulate muscle protein synthesis (MPS), modulate appetite-regulating hormones, and support metabolic health [3].
Sustainable by Design
Pea peptides don’t just nourish bodies—they help protect the planet. Compared to traditional animal-derived proteins like whey or casein, peas require significantly less water and land and generate lower greenhouse gas emissions [4]. For B2B customers, this represents a compelling sustainability narrative that can be passed on to conscious consumers.
| Factor | Pea Protein | Whey Protein |
|---|---|---|
| Water usage | Very low | High |
| Land requirement | Low | Moderate |
| GHG emissions per kg | ~0.4 kg CO₂ | ~10 kg CO₂ |
Pea peptide also supports circular economy practices: leftover starches and fibers from pea protein production are often upcycled into food-grade or industrial applications, further reducing waste.
Muscle-Building Potential
Pea peptides contain a complete profile of essential amino acids, with a notable concentration of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) such as leucine, which plays a key role in mTOR activation and MPS [5]. Though the leucine content is slightly lower than that of whey, studies suggest that pea peptides still effectively promote muscle growth—especially when consumed in adequate doses or combined with other plant peptides.
In a randomized clinical trial, pea protein supplementation produced muscle thickness gains comparable to whey after 12 weeks of resistance training in young men [6]. Peptide forms, with their enhanced digestibility and faster absorption, may offer even greater benefits in post-exercise recovery and lean mass development.
Weight Management & Appetite Regulation
Pea peptides demonstrate notable effects on satiety and body composition. They influence the release of gut-derived satiety hormones such as GLP-1, PYY, and CCK, which help reduce food intake and prolong fullness [7]. This makes them ideal candidates for:
- Functional meal replacements
- Low-calorie protein beverages
- Appetite-control supplements
Several studies report reductions in daily calorie intake and body fat percentage after consistent pea peptide supplementation, positioning them as a clinically relevant ingredient for weight-conscious product lines.
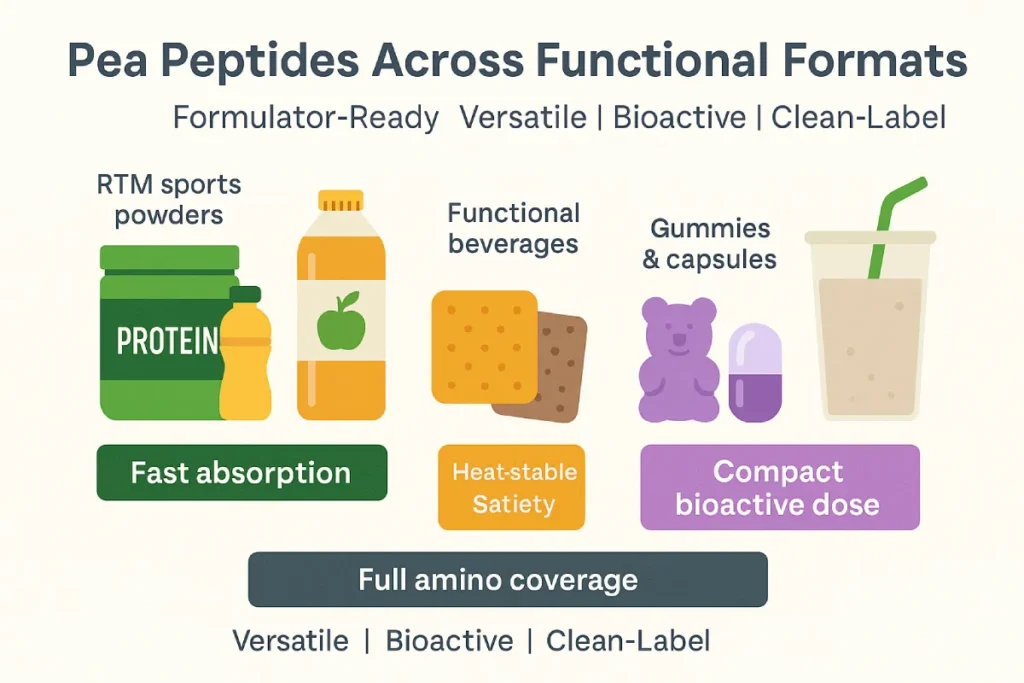
Formulation Opportunities Across Formats
| Application Type | Benefits of Pea Peptides |
|---|---|
| RTM sports powders | Fast absorption, muscle recovery support |
| Functional beverages | Low viscosity, heat-stable, satiety-promoting |
| High-protein snacks | Plant-based positioning, clean-label compliance |
| Gummies & capsules | Compact dosage of targeted bioactive fractions |
| Meal replacement shakes | Full amino acid coverage, sustained energy release |
To support formulators, advanced pea peptides can be offered in standardized molecular weight ranges (e.g., <1kDa or 1–3kDa) or with customized bitterness masking for sensitive applications.
Regulatory and Clean-Label Compliance
Pea peptides are generally recognized as safe (GRAS) in the U.S., widely accepted under EU food laws, and permitted in key Asia-Pacific markets. Their compatibility with Halal, Kosher, Non-GMO, and allergen-free certifications also makes them a low-risk addition for brands operating across multiple regulatory environments.
Permitted health claims (where applicable) may include:
- “Supports muscle recovery after exercise”
- “Promotes feelings of fullness”
- “Contributes to maintenance of lean body mass”
Go-to-Market Messaging for B2B Buyers
As a direct manufacturer and global supplier of full-spectrum functional peptides, we offer more than just ingredients—we deliver science-backed, commercially viable solutions for innovation-driven brands.
- Sustainability meets performance: Align with ESG goals while delivering results in strength, satiety, and metabolic wellness.
- Traceable sourcing + scalable supply: Our large-scale production and integrated QC systems ensure consistent, safe, and high-quality ingredients.
- Tailored peptide solutions: Choose from a portfolio of high-purity pea peptides designed for diverse applications and molecular needs.
- Portfolio synergy: Complement pea peptides with other plant- or marine-based peptides (e.g., soy, rice, ginseng, chlorella) for broader bioactivity or blended systems.
Future Innovation Outlook
The future of pea peptides is being shaped by technology and systems biology:
- AI-guided peptide design: Identifying sequences for enhanced bioactivity or disease-targeted functionality.
- Synergistic blends: Combining pea peptides with postbiotics, prebiotics, or botanicals for holistic weight or metabolic solutions.
- Zero-waste manufacturing: Integrating solid-state fermentation and upcycled biomass valorization.
- Personalized nutrition: Incorporating pea peptide biomarkers into wearables and apps for precision diet planning.
Conclusion: A Smart Choice for Modern Nutrition
Pea peptides offer B2B formulators a rare trifecta—clinically relevant functionality, consumer-demand alignment, and sustainability credentials. Whether you’re developing high-protein beverages, body recomposition supplements, or clean-label functional foods, pea peptides present a safe, scalable, and impactful choice.
As a source manufacturer with deep expertise in bioactive peptide innovation, we are ready to help you build the next generation of plant-based nutritional products—designed for performance, powered by nature.
FAQ
Pea peptides are hydrolyzed protein fragments derived from enzymatic breakdown of pea protein. Unlike regular pea protein isolate or concentrate, peptides have lower molecular weight, are more rapidly absorbed, and exhibit higher bioactivity—especially for muscle recovery and satiety support.
Pea peptides contain all nine essential amino acids, including BCAAs like leucine, making them a complete plant-based protein source. Though leucine levels are slightly lower than whey, they are sufficient to support muscle protein synthesis when used in optimal doses or combined with complementary peptides.
Pea peptides are highly soluble and neutral in taste, making them ideal for use in:
RTM sports nutrition powders
High-protein beverages
Satiety-support supplements
Functional snacks and gummies
Meal replacement systems
They are compatible with both dry and liquid delivery formats.
Yes. Pea peptides are naturally vegan, non-GMO, gluten-free, and free of common allergens such as soy or dairy. They meet clean-label demands and can be certified Halal, Kosher, and Organic depending on the supply chain.
Pea peptides promote satiety by stimulating the release of hormones like GLP-1 and PYY, which help reduce appetite and calorie intake. They are also effective in maintaining lean muscle mass, which is crucial for metabolic health and sustainable weight control.
Compared to whey, casein, or meat-derived proteins, pea peptides require significantly less water and land and generate far fewer greenhouse gas emissions. They are a sustainable choice aligned with ESG goals and carbon-conscious product strategies.
Absolutely. Pea peptides pair well with other plant or marine peptides (e.g., rice, soy, ginseng, fish collagen) to create targeted solutions—for example, muscle recovery blends, metabolic support stacks, or plant-based protein systems with complete amino acid coverage.
Yes. As a source manufacturer and full-spectrum peptide supplier, we provide standard and customized pea peptide profiles tailored to molecular weight, solubility, taste, or application type. We support formulation development, regulatory documentation, and global delivery.
References
- Udenigwe, C. C., & Aluko, R. E. (2012). Food protein-derived bioactive peptides: Production, processing, and potential health benefits. Journal of Food Science, 77(1), R11–R24.
- Grand View Research. (2024). Plant-Based Protein Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report.
- Gilani, G. S., Xiao, C. W., & Cockell, K. A. (2012). Impact of antinutritional factors in food proteins on the digestibility of protein and bioavailability of amino acids. Journal of AOAC International, 95(4), 974–980.
- Poore, J., & Nemecek, T. (2018). Reducing food’s environmental impacts through producers and consumers. Science, 360(6392), 987–992.
- Devries, M. C., & Phillips, S. M. (2015). Supplemental protein in support of muscle mass and health: Advantage whey. Journal of Food Science, 80(S1), A8–A15.
- Babault, N., et al. (2015). Pea proteins oral supplementation promotes muscle thickness gains during resistance training: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial vs. whey protein. JISSN, 12, 3.
- Hall, W. L., et al. (2003). Casein and whey exert different effects on plasma amino acid profiles, gastrointestinal hormone secretion and appetite. British Journal of Nutrition, 89(2), 239–248.