Choosing the Right Peptide Drying Method: Freeze-Drying vs Spray-Drying
As the global peptide market expands, efficient and reliable drying methods have become critical for maintaining product stability, functionality, and bioactivity. Whether you’re launching a nutraceutical brand, scaling OEM peptide production, or optimizing functional food formulations, selecting the right drying technology is a pivotal step in delivering quality peptide ingredients to market.
This article explores two of the most widely used peptide drying methods—freeze-drying and spray-drying—comparing their principles, advantages, limitations, and use cases. Understanding these methods helps B2B buyers, R&D specialists, and formulation teams choose the most suitable process based on product goals, cost efficiency, and peptide stability.
Why Peptide Drying Matters in Functional Nutrition
Peptides are biologically active compounds that are sensitive to temperature, moisture, and oxidation. Without proper drying, peptides risk losing potency, undergoing hydrolysis, or becoming microbiologically unstable. Drying transforms peptides into a stable, easily stored, and transportable powder form, ready for applications ranging from dietary supplements and protein beverages to cosmeceuticals and pharmaceuticals [1].
Two drying techniques dominate industrial peptide production: freeze-drying (lyophilization) and spray-drying. Each offers unique benefits depending on the peptide type and intended application.
Freeze-Drying (Lyophilization): Preserving Peptide Integrity
Freeze-drying involves freezing the peptide solution and then sublimating the ice directly into vapor under vacuum conditions. This low-temperature, low-pressure process is gentle and ideal for preserving bioactivity in heat-sensitive peptides [2].
Key Advantages of Freeze-Drying
- Maximized Peptide Stability: Retains molecular structure, making it ideal for enzymatically hydrolyzed or therapeutic peptides.
- Extended Shelf Life: Minimal residual moisture protects peptides from degradation.
- Suitable for High-Value Formulations: Used in injection-grade peptides, cosmeceuticals, or clinical-grade products.
- Porous Powder Structure: Facilitates rapid reconstitution in liquids.
Limitations
- High Operational Costs: Energy-intensive, longer processing time.
- Low Throughput: Better suited for small to medium-scale production.
- Lower Powder Flowability: Often requires secondary processing for encapsulation or tableting.
Use Cases
Brain peptides, thymus peptides, and injectable oligopeptides. Cosmeceutical powders requiring molecular integrity and reconstitution performance.
Spray-Drying: Scalable and Cost-Efficient for Functional Foods
Spray-drying converts peptide liquids into powder by atomizing them into fine droplets in a hot air chamber. The moisture evaporates instantly, yielding a dry powder with good solubility and flowability [3].
Key Advantages of Spray-Drying
- Fast and Scalable: Ideal for large-volume production with short cycle times.
- Lower Cost: Energy-efficient compared to freeze-drying.
- Uniform Particle Morphology: Produces flowable, easily blendable powders.
- Adaptable Parameters: Temperature, airflow, and feed rate can be adjusted to reduce peptide denaturation.
Limitations
- Potential Loss of Bioactivity: High inlet temperatures may denature certain peptide chains.
- Not Ideal for Thermo-Labile Peptides: Especially those with complex tertiary structures or enzymatic functions.
Use Cases
Collagen peptides for RTD beverages. Soy peptides for protein powders and nutritional supplements. Oyster peptides for capsule formulations.
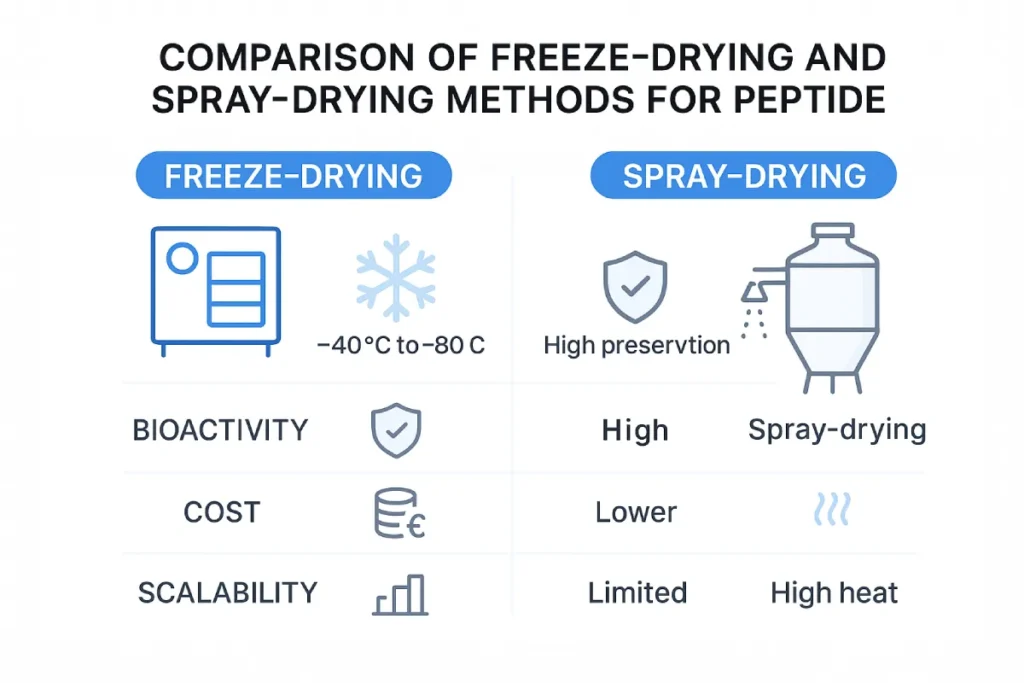
Comparative Table: Freeze-Drying vs Spray-Drying
| Parameter | Freeze-Drying | Spray-Drying |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Sensitivity | Excellent for heat-sensitive peptides | Moderate – heat can degrade some peptides |
| Processing Speed | Slow | Fast |
| Cost | High | Lower |
| Scale | Small to medium batches | Medium to large-scale production |
| Powder Flowability | Poor to moderate | Good |
| Moisture Content | Very low | Low to moderate |
| Application Fit | Pharma, cosmeceuticals, R&D | Functional food, nutrition brands |
Choosing the Right Drying Method for Your Peptide Product
For R&D departments, the primary goal is to preserve peptide structure for functional validation. Freeze-drying is typically preferred in early-stage development or for therapeutic peptides requiring intact bioactivity.
For OEM/ODM manufacturers, spray-drying offers cost-effective scalability, especially for peptides used in sports nutrition, beauty-from-within, or daily supplement lines.
For brand formulators, the decision should consider:
- Product format (capsule, RTD, powder stick)
- Peptide sensitivity
- Desired particle size
- Budget constraints
- Shelf life and reconstitution needs
Innovations in Peptide Drying: What’s Next?
Technological advances are bridging the gap between these two methods. Emerging approaches include:
- Vacuum-assisted spray-drying to reduce peptide exposure to high temperatures.
- Microencapsulation during spray-drying, protecting peptides using carriers like maltodextrin or liposomes.
- Hybrid drying methods combining freeze concentration with spray-drying to optimize stability and efficiency [4].
PEPDOO®: Your Expert Partner in Peptide Powder Manufacturing
At PEPDOO®, we operate both freeze-drying and spray-drying production lines, allowing us to adapt to diverse product needs:
- Custom drying solutions for over 50 types of functional peptides.
- Process validation to ensure bioactive retention.
- Support for formulation development, including solubility and encapsulation optimization.
Strategic Drying Choices: Aligning Technology with Product and Market Goals
Selecting the right peptide drying method is not just a technical decision—it’s a strategic one. It directly affects product quality, stability, and commercial viability. Freeze-drying offers unmatched protection for sensitive bioactive peptides, while spray-drying provides scalability and cost efficiency for nutrition applications.
As a B2B stakeholder in the peptide space, aligning your drying strategy with your product vision ensures your peptide offerings are effective, stable, and market-ready.
🚀 Looking to Optimize Your Peptide Formulation Strategy?
Partner with PEPDOO® to select the right drying method—freeze-dried or spray-dried—for your product line.
🔹 Request a technical datasheet
🔹 Ask for peptide samples
🔹 Schedule a consultation with our formulation experts
FAQ
Freeze-drying (lyophilization) is the preferred method for heat-sensitive peptides. It avoids high-temperature exposure by using low-temperature sublimation, preserving the peptide’s structural and functional integrity.
Generally, no. Spray-drying involves heat, which may degrade high-purity peptides. It's better for food-grade or cosmetic applications.
Freeze-dried peptides: ~1–3%. Spray-dried peptides: ~3–6%, depending on process conditions and excipients.
Freeze-dried powders rehydrate quickly due to their porous texture. Spray-dried powders may need surfactants for full solubility.
Yes. PEPDOO® provides tailored solutions for drying time, moisture level, particle size, and active retention.
Freeze-drying: 2–4 days per batch. Spray-drying: 4–8 hours per batch. Timelines vary by volume and customization.
Both methods can be GMP-compliant. Freeze-drying is preferred for pharmaceutical-grade products due to structural preservation.
Common carriers: maltodextrin, trehalose, cyclodextrins, and plant-based gums. These help with solubility and protection.
Yes—vacuum spray-drying, microencapsulation, and hybrid freeze + spray methods are emerging for better stability and efficiency.
Yes. Spray-dried peptides are more uniform and less odorous. Freeze-dried peptides may retain more bioaroma or look irregular.

References
- Harnkarnsujarit, N., & Charoenrein, S. (2011). Effect of Water Activity on Molecular Structure and Stability of Peptide Powders. Food Research International, 44(4), 1004–1013.
- Tang, X., & Pikal, M. J. (2004). Design of Freeze-Drying Processes for Pharmaceuticals: Practical Advice. Pharmaceutical Research, 21(2), 191–200.
- Masters, K. (2002). Spray Drying Handbook. 5th ed. Longman Scientific & Technical.
- Gharsallaoui, A., Roudaut, G., Chambin, O., Voilley, A., & Saurel, R. (2007). Applications of Spray-Drying in Microencapsulation of Food Ingredients. Food Research International, 40(9), 1107–1121.