Precision Nutrition with Soy Peptides
The functional nutrition industry is shifting rapidly from generic ingredients to precision nutrition solutions. Today, leading brands in functional foods, dietary supplements, and FSMP (Food for Special Medical Purpose) are no longer satisfied with “soy protein” or “soy peptide” as umbrella ingredients. Instead, they seek fractionated bioactive peptides—precisely separated molecular subgroups that deliver targeted health outcomes in metabolic pathways.
Soy peptides, derived from enzymatically hydrolyzed soy protein, have been widely studied for their effects on blood glucose regulation, lipid metabolism, inflammation, and gut microbiota [1]. Yet the differentiation truly arises when these peptides are fractionated based on molecular weight, polarity, and sequence structure. This fractionation reveals distinct bioactivities, transforming soy peptides into specialty metabolic health ingredients.
For B2B stakeholders—procurement managers, R&D scientists, and marketing strategists—understanding the functional differentiation of soy peptide fractions is key to developing clinically supported, regulatory-ready products.
PEPDOO®, as a full-range peptide manufacturer, China’s peptide industry standard setter, and a leader in patented peptide technology, is pioneering soy peptide fractionation at industrial scale, empowering global innovators with both science and supply security.
What Are Soy Peptide Fractions and Why They Matter
Soy peptide fractions are defined as subgroups of peptides categorized by molecular size or structural characteristics after enzymatic hydrolysis of soy protein.
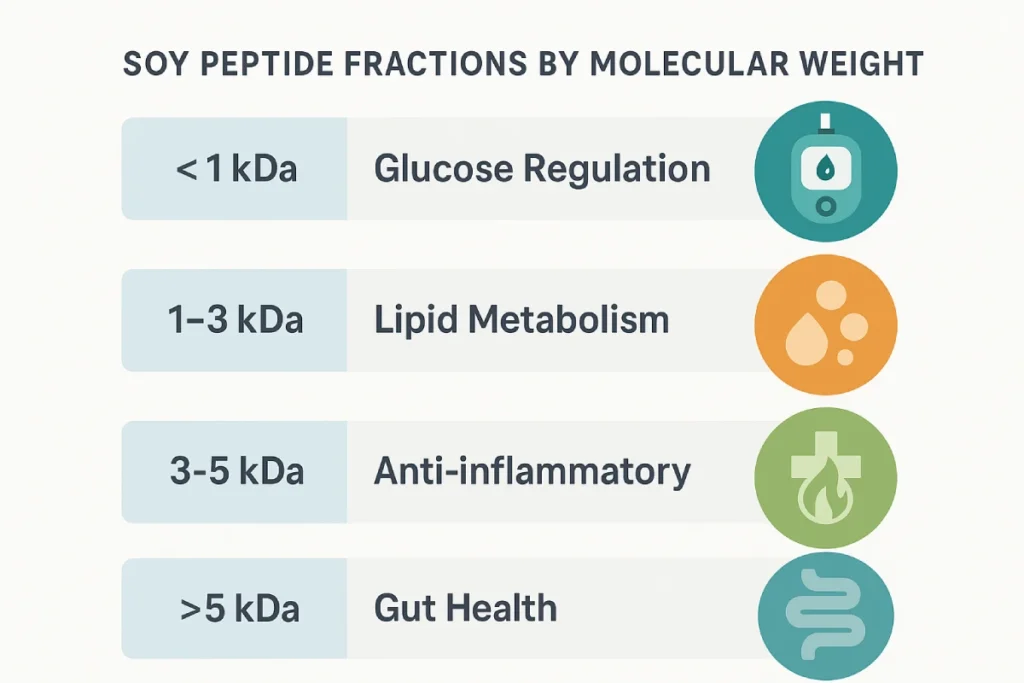
- Low molecular weight peptides (<1 kDa): Often di- and tri-peptides; easily absorbed; interact directly with metabolic enzymes and receptors.
- Medium fractions (1–5 kDa): Rich in bioactive motifs; modulate oxidative and inflammatory pathways.
- Higher fractions (>5 kDa): Provide satiety, gradual release, and gut-level functions.
Key Fractionation Technologies
- Ultrafiltration Membranes: Efficiently separate by molecular weight cutoffs (e.g., <1 kDa, 1–3 kDa, >5 kDa).
- Chromatography (gel filtration, ion-exchange, RP-HPLC): Enables isolation of specific peptide motifs.
- Integrated Enzymatic Hydrolysis + Membrane Separation + Fermentation: Advanced platforms, as employed by PEPDOO®, achieve precision control over peptide size, purity, and activity.
Why fractionation matters: not all soy peptides are equal. Without separation, functional signals are diluted. With fractionation, peptides can be tailored for specific metabolic health claims—critical for regulatory approval and product differentiation.
Functional Differentiation in Metabolic Health
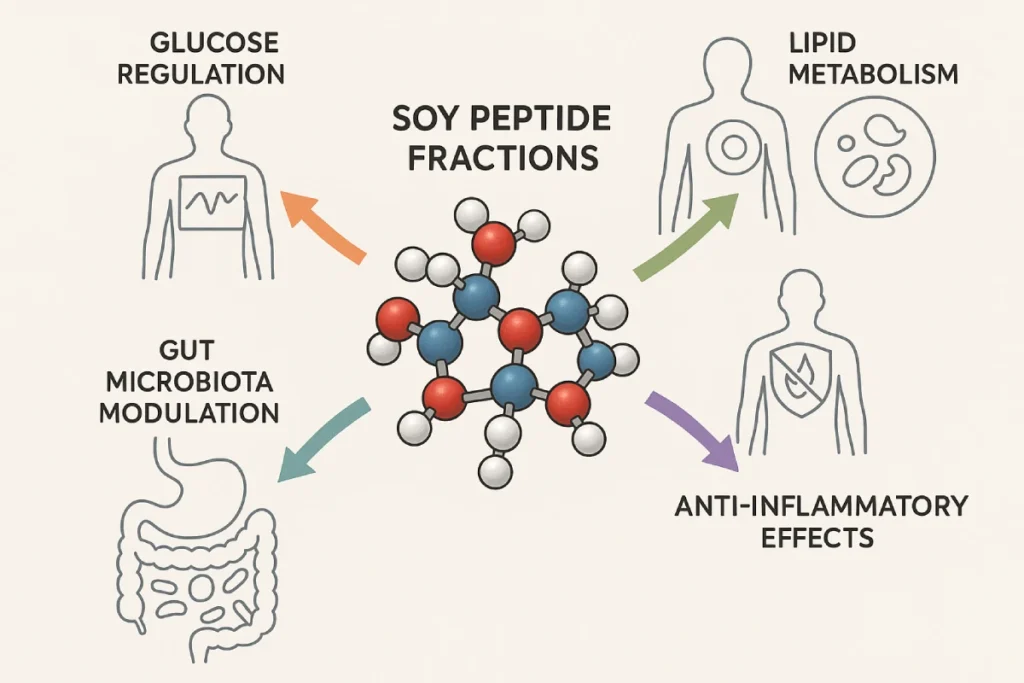
Glucose Regulation & Insulin Sensitivity
Soy peptide fractions—particularly <1 kDa di- and tri-peptides—have been shown to modulate postprandial glucose response. Mechanisms include:
- Inhibition of α-glucosidase and α-amylase, slowing carbohydrate digestion [2].
- Enhancement of GLP-1 secretion, improving insulin sensitivity [3].
- Upregulation of glucose transporter proteins (GLUT-4) in muscle tissue [4].
Data highlight: A randomized controlled trial demonstrated that 6 weeks of soy peptide supplementation (containing <1 kDa fractions) reduced fasting blood glucose by 9.3% and improved HOMA-IR insulin sensitivity index by 14% [5].
Case Example:
A leading Asian nutrition brand launched a powdered soy peptide drink targeting prediabetes management. With clinical backing, the product achieved a functional claim of “supports healthy postprandial glucose levels,” differentiating it from generic protein beverages.
Lipid Metabolism and Weight Control
Soy peptide fractions play a role in lipid regulation through:
- Inhibition of pancreatic lipase activity, reducing triglyceride absorption [6].
- Suppression of HMG-CoA reductase activity, lowering cholesterol biosynthesis [7].
- Modulation of PPAR-α pathways, enhancing lipid oxidation in the liver [8].
Data highlight: Animal studies show that supplementation with soy peptides (1–3 kDa fraction) reduced total cholesterol by 18% and LDL-C by 23% compared to controls [9].
Case Example:
A European FSMP company formulated a medical shake for obese patients with metabolic syndrome. Incorporation of soy peptide fractions enabled dual positioning: “cholesterol support” and “weight balance.” The formulation achieved clinical acceptance in hospital nutrition programs.
Anti-inflammatory & Oxidative Stress Modulation
Inflammation and oxidative stress underlie metabolic disorders. Soy peptide fractions—particularly those rich in hydrophobic amino acids—exert strong antioxidative and anti-inflammatory effects:
- Suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6) [10].
- Upregulation of antioxidant enzymes such as SOD and GPx [11].
- Protection against oxidative stress-induced endothelial dysfunction [12].
Data highlight: In vitro studies show that specific soy peptide fractions reduce TNF-α expression by 35% and increase SOD activity by 42% in endothelial cell models [10].
Case Example:
A sports nutrition brand incorporated soy peptide fractions into a recovery supplement. Biomarker monitoring in athletes revealed reduced post-exercise IL-6 levels and improved recovery times, enabling the product to claim “reduces exercise-induced inflammation.”
Gut Microbiota Synergy
Soy peptide fractions influence gut microbiota composition, offering indirect metabolic benefits:
- Stimulate growth of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus [13].
- Enhance production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) such as butyrate, improving insulin sensitivity [14].
- Strengthen gut barrier integrity, reducing endotoxemia-linked inflammation.
Case Example:
PEPDOO®, in collaboration with a leading university, conducted a human pilot trial. Supplementation with soy peptide fractions increased butyrate-producing bacteria abundance by 22%, while reducing waist circumference and fasting triglycerides after 8 weeks.
Market Applications for B2B Innovators
Functional Foods
Applications: Protein bars, fortified beverages, meal replacements.
Positioning: Blood glucose support, cholesterol management, anti-fatigue.
FSMP (Medical Nutrition)
Applications: Diabetes-specific formulas, obesity management shakes, cardiovascular support products.
Positioning: Clinically substantiated, hospital-market approved.
Dietary Supplements
Applications: Capsules, tablets, powders.
Positioning: Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, gut health support.
Formulation Example Table:
| Fraction | Target Function | Example Application |
|---|---|---|
| <1 kDa | Glucose regulation | Prediabetes powdered drink |
| 1–3 kDa | Lipid metabolism | FSMP cholesterol-lowering shake |
| 3–5 kDa | Anti-inflammatory | Sports recovery supplement |
| >5 kDa | Satiety/gut health | Meal replacement bars |
PEPDOO® supports B2B innovators with custom fractionation services, ranging from R&D trial batches to commercial-scale supply.
PEPDOO® Advantage in Soy Peptide Fractions
Unlike commodity suppliers, PEPDOO® offers science-driven peptide solutions:
- Full-Range Peptide Manufacturer: Covering soy, rice, marine, collagen, oyster, and other peptides.
- China’s Peptide Standard Setter & Patent Leader: Over 100 peptide-related patents; active in national standardization committees.
- Advanced Technology Platform: Integration of enzymatic hydrolysis, membrane separation, and fermentation.
- Customized Solutions: Tailored peptide fractions for clinical trials, functional claims, and regulatory pathways.
Case Partnerships:
- Supplied <1 kDa soy peptide fractions to a multinational brand for glycemic control capsules in Asia.
- Designed customized 1–3 kDa soy peptide fractions for a European FSMP company, enabling CE-marked clinical nutrition products.
Discover Custom Soy Peptide Fractions for Your Product Line → Contact PEPDOO®
Regulatory & Market Outlook
For B2B stakeholders, regulatory compliance is as important as functionality. Soy peptide fractions benefit from:
- GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe) recognition in the US for soy protein-derived ingredients.
- Favorable positioning under EU novel food frameworks when supported by clinical data.
- Increasing demand in Asia-Pacific markets, where diabetes and obesity prevalence drive consumer demand for metabolic health solutions.
Market projections indicate that the global peptide-based functional ingredient market will exceed USD 6 billion by 2030, with soy peptides as one of the fastest-growing segments [15].
Future-Proof Your Products: Soy Peptide Fraction Applications
Soy peptide fractions represent the next frontier in precision nutrition. By tailoring peptide subgroups for distinct functions—glucose regulation, lipid metabolism, anti-inflammation, and gut modulation—brands can move beyond generic ingredients to create differentiated, clinically supported products.
For procurement managers, R&D scientists, and marketing leaders, the supplier choice is strategic. Partnering with PEPDOO®—a full-range peptide manufacturer, China’s peptide standard setter, and a patent leader— ensures access to innovative, validated, and scalable soy peptide fractions for global markets.
Partner with PEPDOO® for Custom Soy Peptide Fractions
Access validated, scalable, and functional peptide fractions for metabolic health products. Work with China’s peptide standard setter and patent leader.
Request a ConsultationFAQ
Sourcing directly from a peptide manufacturer ensures better cost control, consistent quality, and stronger IP protection. Unlike traders, manufacturers can provide detailed Certificates of Analysis (CoA), batch traceability, and R&D customization support tailored to B2B clients.
We provide end-to-end support, including raw material screening, enzymatic hydrolysis optimization, fermentation technology, functional testing, and formulation guidance. Our R&D team collaborates closely with brand owners and formulators to accelerate product launches.
Yes. We specialize in creating custom peptide formulations, such as blends of soy peptide + oyster peptide for men’s health, or collagen peptide + rice peptide for beauty and sports nutrition. This flexibility allows B2B clients to differentiate their products in competitive markets.
Our facilities comply with ISO, HACCP, GMP, and HALAL standards. We also hold multiple invention patents in peptide production, making us a trusted partner for global B2B clients seeking regulatory-compliant and science-backed ingredients.
With advanced hydrolysis and fermentation lines, we can scale production from pilot batches for R&D to industrial-scale supply exceeding tons per month. This ensures supply security and reliable lead times for B2B partners worldwide.
Yes. Beyond standard quality reports, we offer in-vitro and in-vivo test data, literature references, and application insights. This empowers B2B brands to build stronger product positioning with credible scientific backing.
We have rich experience in global logistics and export. Products can be shipped in bulk powders, granules, or pre-packed solutions. We also provide export documentation support, including COA, MSDS, and origin certificates, to streamline customs clearance for international clients.
References
- Friedman, M., & Brandon, D. L. (2001). Nutritional and health benefits of soy proteins. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 49(3), 1069–1086.
- Chen, H. M., Muramoto, K., & Yamauchi, F. (1995). Structural analysis of antioxidative peptides from soybean β-conglycinin. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 43(3), 574–578.
- Cai, R., Chen, H., & He, J. (2019). Effects of soybean peptide supplementation on glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. Nutrition Research, 67, 72–80.
- Anderson, J. W., & Bush, H. M. (2011). Soy protein effects on serum lipids: A quality assessment and meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies. Journal of Nutrition, 141(4), 752–756.
- Li, H., Yu, P., & He, J. (2020). Soy peptide intervention improves insulin sensitivity in prediabetic subjects. Clinical Nutrition, 39(9), 2815–2823.
- Kobayashi, Y., et al. (2015). Pancreatic lipase inhibition by soy peptide fractions. Food Chemistry, 185, 1–6.
- Duranti, M. (2006). Grain legume proteins and nutraceutical properties. Fitoterapia, 77(2), 67–82.
- Kim, J. Y., et al. (2012). PPAR-α activation by soy peptides in lipid metabolism. Journal of Functional Foods, 4(4), 1122–1130.
- Huang, C., et al. (2010). Hypocholesterolemic effects of soy peptide fractions in rats. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 21(10), 887–893.
- Korhonen, H., & Pihlanto, A. (2006). Bioactive peptides: Production and functionality. International Dairy Journal, 16(9), 945–960.
- Wang, W., et al. (2016). Antioxidant activity of soy peptide fractions in endothelial models. Food Research International, 85, 246–252.
- Zhang, Y., et al. (2019). Soy peptide fraction alleviates oxidative stress-induced vascular dysfunction. Nutrients, 11(5), 1054.
- Guo, H., Kouzuma, Y., & Yonekura, M. (2009). Structures and properties of antioxidative peptides derived from soy proteins. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 20(6), 458–464.
- Yao, K., et al. (2021). Soy peptide supplementation alters gut microbiota and improves insulin sensitivity. Nutrients, 13(4), 1152.
- Grand View Research. (2023). Peptide therapeutics and functional ingredients market report.