1. Why Peptide Characterization Matters
Whether you are formulating a collagen peptide beverage, validating an API such as teriparatide, or negotiating a toll‑manufacturing agreement, rigorous peptide characterization is the non‑negotiable passport to regulatory approval, supply‑chain confidence, and brand equity. ICH Q6B explicitly states that biotechnology products must be defined by “physicochemical properties, purity, and impurities” before lot release [1]. Skipping—or under‑specifying—analytics drives costly re‑works, recalls, and GMP warnings.
Primary keyword integration: peptide characterization, peptide QC, HPLC peptide analysis.
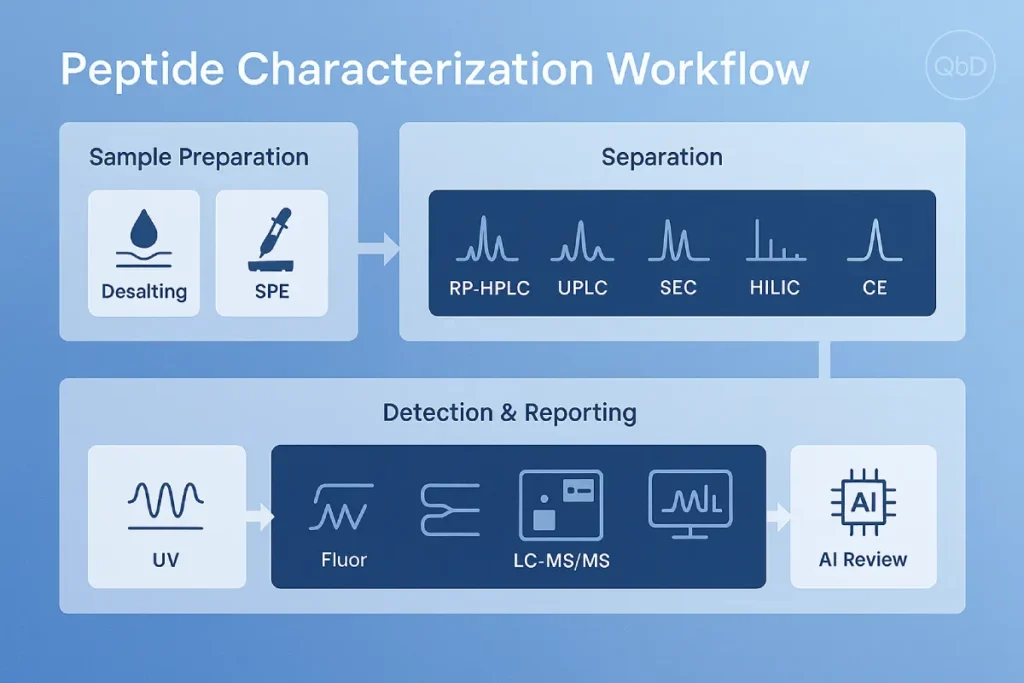
2. An End‑to‑End Analytical Workflow
- Sample preparation – desalting, solid‑phase extraction, or spin‑dialysis to remove salts and excipients that suppress ionization.
- Separation – chromatographic or electrophoretic partitioning to reduce mixture complexity.
- Detection – UV, fluorescence, or increasingly high‑resolution LC‑MS/MS.
- Data analysis & reporting – spectral deconvolution, database matching, acceptance‑criteria decision.
Each step should be developed under a quality‑by‑design (QbD) umbrella: define critical quality attributes (e.g., purity ≥ 95 %), establish system suitability, and lock validated parameters into SOPs.
3. Chromatography: Still the Workhorse
3.1 Reversed‑Phase HPLC (RP‑HPLC)
- Use‑case: Lot‑release purity and process monitoring.
- Why it works: Hydrophobic C18 columns exploit peptide side‑chain interactions; gradient elution separates by hydrophobicity—ideal for HPLC peptide analysis.
- Detectors: UV 214 nm for backbone amides; diode‑array for impurity profiling.
3.2 Ultra‑Performance LC (UPLC)
Sub‑2 µm particles shorten run‑time to < 5 min—key for high‑throughput peptide QC in CDMO environments.
3.3 Size‑Exclusion Chromatography (SEC)
Screens aggregation in collagen or whey peptide concentrates. Aggregates > 10 kDa are red flags for solubility and immunogenicity.
3.4 Hydrophilic‑Interaction LC (HILIC)
Retains highly polar or glycosylated peptides (e.g., glycopeptide growth factors).
3.5 Ion‑Exchange (IEX) & Mixed‑Mode
Differentiates charge variants—useful when post‑translational modifications (PTMs) shift pI.
4. Capillary Electrophoresis (CE) & CE‑MS
Capillary Zone Electrophoresis offers >100 k theoretical plates, ultra‑low sample consumption, and is orthogonal to RP‑HPLC. Hyphenation with MS (CE‑MS) couples the resolution of electrophoresis with peptide mass spectrometry for charge‑variant fingerprints in under 10 min [8]. Emerging imaged CIEF‑MS platforms deliver isoelectric maps with on‑line MS confirmation—excellent for biosimilar comparability.
5. Mass Spectrometry: The Structural Decoder Ring
5.1 Ionization Choices
- Electrospray Ionization (ESI): Soft, solution‑like; mainstream for LC‑MS.
- MALDI: Tolerant to salts, great for imaging and high‑throughput screens.
5.2 Analyzer Landscape
| Analyzer | Resolution | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| Quadrupole | 30 k | Targeted SRM/PRM assays |
| Q‑TOF | 60–100 k | Discovery, PTM scouting |
| Orbitrap | 120–500 k | Precision mass confirmation |
| FT‑ICR | >500 k | De novo sequencing, isotopic fine structure |
5.3 LC‑MS/MS Workflows
- Bottom‑up: Enzymatic digest → peptide mapping → PTM localization.
- Top‑down / Native MS: Intact analysis preserves non‑covalent interactions—critical for peptide‑drug conjugates and epitope mapping [11].
5.4 Ion‑Mobility Enhancements
Trapped Ion Mobility Spectrometry (TIMS) adds a fourth dimension—collision cross‑section (CCS)—separating isobaric species and boosting ID rates. Time‑Segmented Acquisition (Seg) on TIMS‑TOF expands phosphopeptide coverage by 30 % without runtime penalty [2]. Bruker’s latest 4D‑Proteomics suite even integrates glyco‑PASEF modes for intact glycopeptide profiling [3].
5.5 Next‑Gen High‑Speed MS
Thermo Fisher’s Orbitrap Astral™ claims 20 Hz sequencing speed and sub‑ppm mass accuracy, enabling single‑cell peptideomics and ultra‑fast stability studies [4].
6. Quantitative Strategies
| Strategy | Principle | Best‑fit Scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| Label‑free peak area (LFQ) | Intensity across runs | Process comparability, exploratory screens [9] |
| SILAC | Stable‑isotope metabolic labeling | Cell‑culture mechanism studies |
| Isobaric tags (TMT/iTRAQ) | Reporter ions released in MS2 | Multiplexed stress‑test lots |
Consistency checks: %RSD < 15 % for QC peptides, dynamic range ≥ 3 log fold.
7. Orthogonal & Supporting Techniques
| Technique | Insight | Why it matters |
|---|---|---|
| NMR | 3‑D conformation in solution | Confirms bioactive helix vs coil in marine collagen mini‑peptides |
| Circular Dichroism / FTIR | Secondary structure | Rapid excipient compatibility screens |
| Amino‑Acid Analysis (AAA) | Molar composition | Detects hydrolysis drift during scale‑up |
| Edman or enzymatic sequencing | Terminal residue verification | Small therapeutic peptides (<20 aa) where MS may undersample |
8. Case Studies
8.1 Teriparatide API Impurity Profiling
A 2025 LC‑HRMS method quantified six low‑level side products at < 0.3 % w/w, meeting pharmacopeial thresholds [6]. Result: 15 % faster lot release and smoother ANDA filing.
8.2 Dairy Casein Macropeptide (CMP) Authentication
Top‑down UPLC‑Q‑TOF detected 51 intact CMPs and 159 derived fragments, flagging heat‑induced glycation early in pilot spray‑drying [7].
8.3 Spatial Peptideomics in Skin Patches
MALDI‑TIMS imaging with the SIMSEF workflow resolved palmitoylated anti‑wrinkle peptides directly in hydrogel matrices—guiding uniformity specs for leave‑on masks [5].
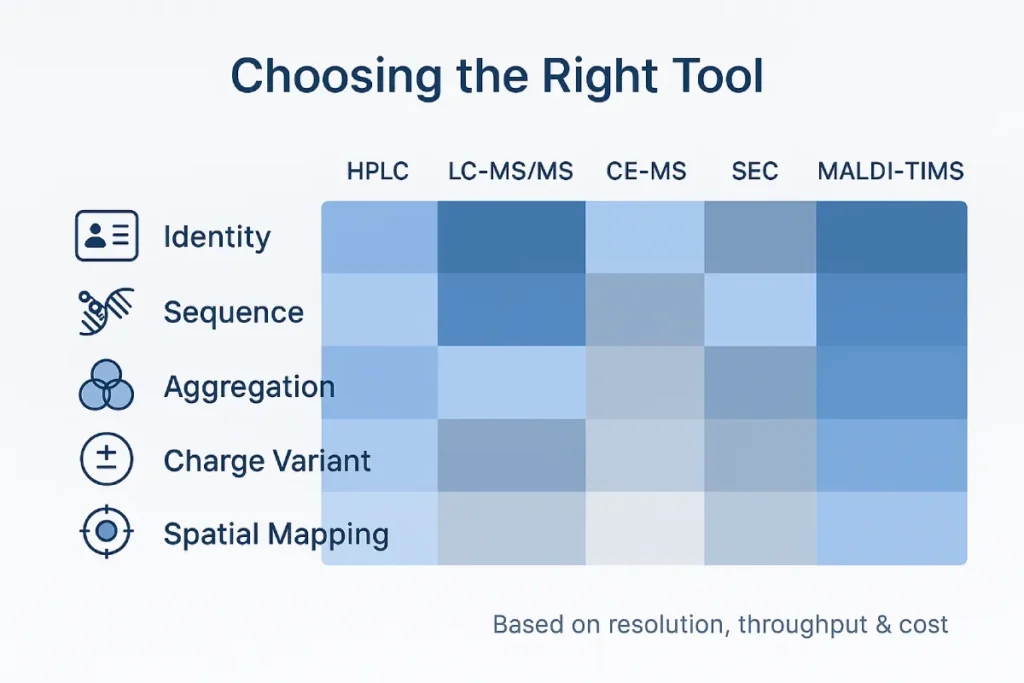
9. Choosing the Right Tool: A Decision Matrix
- Identity & Purity: RP‑HPLC + UV; escalate to LC‑MS/MS if unknown peaks > 0.1 %.
- Sequence & PTMs: High‑resolution Orbitrap or Q‑TOF with data‑dependent acquisition; add TIMS for isomers.
- Charge Heterogeneity: icIEF‑MS or CE‑MS.
- Aggregation: SEC‑MALS or Native MS.
- Spatial Localization: MALDI‑TIMS imaging.
Tip: Combine orthogonal methods for regulatory robustness—ICH reviewers love confirming the same CQAs via two unrelated techniques.
10. Validation & Compliance Essentials
| Parameter | Typical Acceptance Criterion |
|---|---|
| Specificity | Baseline separation of main + impurity peaks (Rs ≥ 1.5) |
| Accuracy | 95–105 % recovery across 3 spiking levels |
| Precision | %RSD ≤ 5 % repeatability, ≤ 10 % intermediate precision |
| LOD/LOQ | S/N ≥ 3 (LOD) or 10 (LOQ) |
| Robustness | No > 5 % drift when pH ± 0.2 or temp ± 5 °C |
| Data Integrity | Audit trails, ALCOA+, 21 CFR Part 11 compliance |
Automated spectral‑library QC and AI‑assisted de novo tools such as Casanovo reduce review time by 40 % and mitigate manual mis‑annotation risk [10].
11. Future Outlook
- Microfluidic LC‑MS chips enabling at‑line release testing in continuous bioprocessing.
- Cloud native analytics—secure data lakes feeding dashboards for global QC harmonization.
- Greener ionization sources (nano‑ESI at nL min−1) cutting solvent by 90 %.
- Native MS‑integrated docking simulations bridging in‑silico screening and real‑world conformations [11].
12. Key Takeaways for B2B Stakeholders
- Speed with confidence: UPLC + Orbitrap/MS can slash batch turnaround from days to hours without sacrificing data quality.
- Regulatory alignment: Build methods around ICH Q6B from day 1 to avoid retro‑fit headaches.
- Future‑proof your lab: Plan for ion‑mobility and AI‑driven analytics—clients will soon expect 4‑D peptide fingerprints, not just mass/retention time.
Need a custom method or an outsourced stability study?
Contact our peptide analytics team for a feasibility discussion within 24 hours.
FAQ
Peptide characterization refers to the suite of analytical methods used to determine a peptide’s identity, purity, sequence, structure, and modifications. It is essential for ensuring batch consistency, regulatory compliance, and bioactive function in pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and cosmeceutical products.
The most widely used techniques include:
- RP‑HPLC for purity and retention profiling
- LC‑MS/MS for sequence and post‑translational modification (PTM) analysis
- SEC for aggregation and size profiling
- CE or CE‑MS for charge variant distribution
- NMR or Circular Dichroism for secondary structure analysis
LC‑MS/MS enables fragmentation‑based sequencing of peptides. By analyzing the fragmentation pattern (MS2 spectra), scientists can confirm amino acid order, detect PTMs (e.g., phosphorylation), and differentiate isobaric species when combined with ion‑mobility MS.
HPLC is a robust tool for assessing purity, but not sufficient alone for identity verification. It should be complemented by mass spectrometry (MS), which provides molecular mass accuracy and structural confirmation.
- Orbitrap offers ultra‑high resolution (≥500k) and is ideal for de novo sequencing and intact mass analysis.
- Q‑TOF is excellent for routine LC‑MS/MS with fast scan speeds and moderate resolution.
Your choice depends on whether your use‑case prioritizes depth, speed, or budget.
Yes. Native mass spectrometry and SEC coupled with MALS or MS can detect aggregates or multimers in peptide formulations. This is especially important in high‑concentration APIs or injectable peptide drugs.
- ICH Q6B: Specifies requirements for biotechnological products' analytical testing
- USP <509>: Covers peptide content and identification for pharmaceutical‑grade materials
- 21 CFR Part 11: Governs electronic data integrity for cGMP environments
Revalidation is recommended:
- Annually or after significant process changes
- When changing analytical platforms or columns
- If non‑conformities appear in product batches
ICH Q2(R2) outlines the principles of method validation including specificity, precision, accuracy, LOD/LOQ, and robustness.
Ion mobility separates ions by their shape and charge (collision cross‑section), adding a 4th dimension to LC‑MS data. It improves identification of isomeric peptides and increases proteome depth in complex mixtures.
Yes. Microfluidic LC‑MS chips and label‑free UV or FTIR‑based sensors are emerging for real‑time, at‑line, or on‑site quality control. These tools are especially valuable in continuous manufacturing environments.
References
- ICH Q6B: Specifications—Test Procedures and Acceptance Criteria for Biotechnological/Biological Products. (2018). [1]
- Optimized Time‑Segmented Acquisition Expands Peptide and Protein Coverage on TIMS‑TOF. Journal of Proteome Research, 2025. [2]
- Bruker Advances CCS‑Enabled 4D‑Proteomics timsTOF Solutions. Press release, 2024. [3]
- Orbitrap Astral Zoom Mass Spectrometer Applications. Thermo Fisher Scientific, 2023. [4]
- On‑Tissue Dataset‑Dependent MALDI‑TIMS‑MS² Bioimaging. Nature Communications, 2024. [5]
- Validation of LC‑HRMS for Peptide Impurity Quantification in Teriparatide Products. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 2025. [6]
- Targeted Detection of Casein Macropeptide Variants by RP‑HPLC‑MS. Food Chemistry, 2023. [7]
- Capillary Electrophoresis–Mass Spectrometry. Wikipedia, updated 2025. [8]
- Protocols for Label‑Free LC‑MS/MS Proteomic Analysis. In Methods in Enzymology (2024). [9]
- Sequence‑to‑Sequence Translation from Mass Spectra to Peptides with Casanovo. Nature Communications, 2024. [10]
- Native MS Elucidates Epitope Interfaces of Transient Protein–Protein Interactions. Chemical Communications, 2024. [11]