Why Purification Matters in Peptide Manufacturing
In the world of functional peptides—whether for sports nutrition, cosmeceuticals, or medical applications—purity is non-negotiable. Peptides produced via enzymatic hydrolysis or recombinant synthesis often require rigorous downstream purification to meet bioactivity, safety, and regulatory standards. Among various purification technologies, membrane filtration has emerged as a pivotal method, prized for its scalability, selectivity, and relatively low operational cost.
This article explores membrane filtration in the context of peptide purification, with a balanced look at its benefits and drawbacks. Whether you’re a product developer, procurement specialist, or formulation scientist, understanding membrane processes can help you optimize raw material selection, vendor qualification, and even your own manufacturing decisions.
What is Membrane Filtration?
Membrane filtration refers to a pressure-driven separation process using semi-permeable membranes to remove specific components based on size, charge, or molecular interactions. In peptide processing, the goal is typically to remove unwanted macromolecules (such as enzymes or undigested proteins) or to fractionate peptides based on molecular weight.
There are three main classes of membrane filtration used in peptide purification:
- Microfiltration (MF): Removes large particles and microbes.
- Ultrafiltration (UF): Separates peptides based on molecular weight; typically effective for peptides <10 kDa.
- Nanofiltration (NF): Useful for separating salts and smaller molecules.
The defining parameter of any membrane is its molecular weight cut-off (MWCO), which determines what size molecules are retained or passed through. Materials such as polyethersulfone (PES), polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), and cellulose acetate are commonly used, each with specific hydrophilicity, durability, and chemical compatibility.
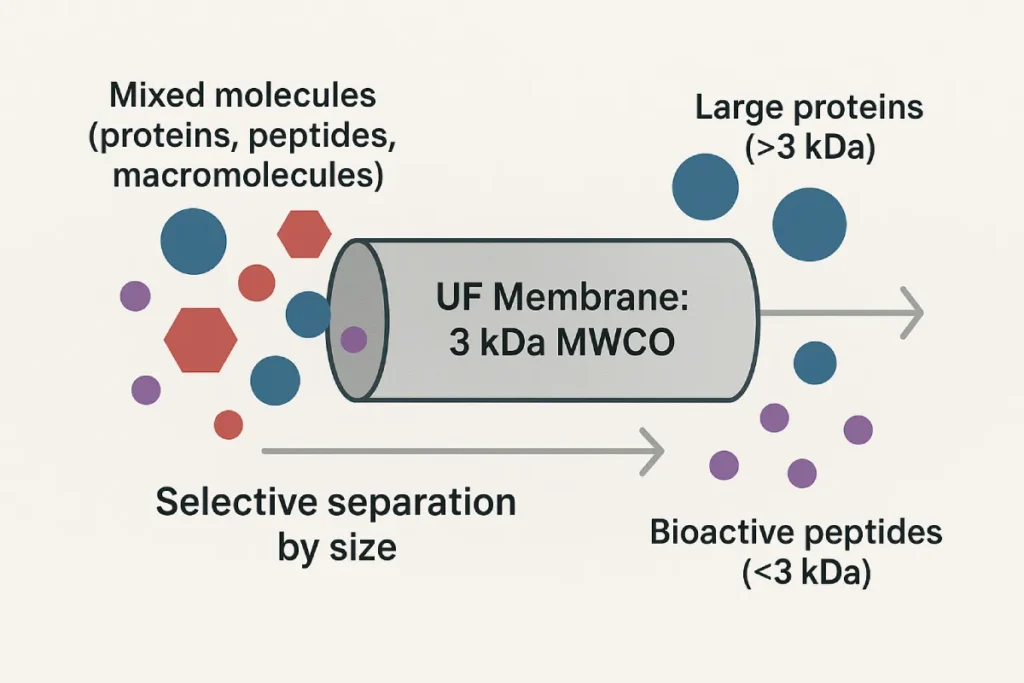
Applications in Peptide Purification
Membrane filtration is applied at multiple points in the functional peptide production pipeline, particularly after enzymatic hydrolysis. It is widely used to:
- Remove proteases and residual protein fragments
- Concentrate peptides to target bioactive ranges (e.g., 500–3000 Da)
- Desalt or exchange buffers for improved formulation compatibility
- Fractionate peptides based on size for tailored biofunctions (e.g., ACE inhibition, antioxidant activity)
For example, ultrafiltration is critical in the production of collagen peptides, casein peptides, and marine-derived oligopeptides, enabling the manufacturer to control both molecular weight distribution and bioactivity profiles [1].
Advantages of Membrane Filtration
✅ Scalable and Continuous
Unlike batch chromatography, membrane systems can be integrated into continuous peptide manufacturing lines, facilitating large-scale production with minimal interruptions.
✅ Non-Thermal and Gentle
Because membrane filtration operates at moderate temperatures and without aggressive chemicals, it preserves the structure and activity of delicate bioactive peptides.
✅ Cost-Efficient
Membrane filtration uses less solvent and energy compared to chromatographic techniques. For peptide manufacturers, this means lower production costs and improved sustainability metrics.
✅ Tunable and Versatile
By selecting membranes with the appropriate MWCO, peptide producers can fine-tune peptide profiles to meet formulation requirements for RTD beverages, capsules, or topicals.
✅ Integratable in Full-Process Manufacturing
Membrane systems are easily integrated into automated lines involving enzymatic hydrolysis, heat inactivation, and spray drying, making them ideal for manufacturers offering one-stop peptide solutions.
Pitfalls and Limitations
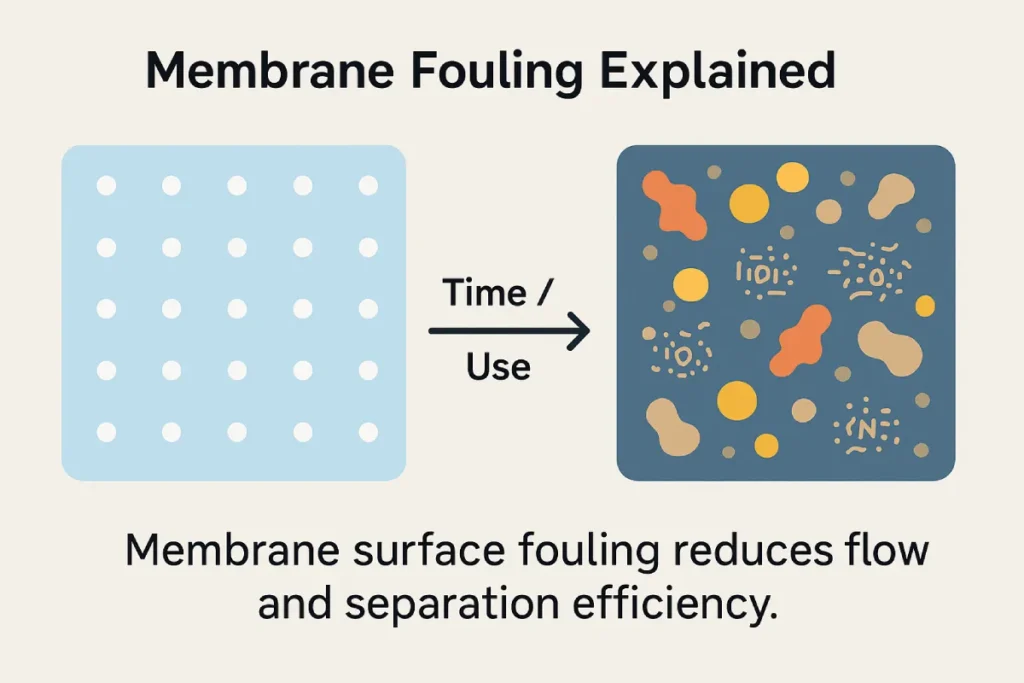
⚠️ Membrane Fouling
Over time, peptide residues, lipids, or minerals can accumulate on the membrane surface, reducing flux and efficiency.
⚠️ Low Resolution Around MWCO
When peptide fragments hover near the MWCO threshold, partial retention or passage can occur, resulting in overlapping peptide profiles.
⚠️ Peptide Loss
Some valuable low-molecular-weight peptides may be lost in the permeate or adsorbed onto the membrane, reducing product potency.
⚠️ Batch-to-Batch Variation
Changes in feedstock quality, pH, or membrane age can lead to batch inconsistency.
⚠️ Material Compatibility Issues
Certain peptides may interact unfavorably with membrane materials, leading to chemical degradation or leaching [2].
Comparison with Other Purification Methods
| Method | Resolution | Cost | Scalability | Solvent Use | Bioactivity Preservation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Membrane Filtration | Moderate | Low | High | Low | High |
| Chromatography | High | High | Moderate | High | Variable |
| Precipitation | Low | Low | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
Best Practices for B2B Peptide Applications
- Choose the Right MWCO: Match the application’s target bioactivity and size range.
- Control Operating Parameters: Optimize pressure, temperature, and crossflow rate.
- Validate Recovery Rates: Ensure peptide yields remain consistent.
- Use Multi-Stage Filtration: Combine membranes for tighter separation.
- Maintain Cleanliness: CIP routines and membrane lifespan tracking are essential.
Future Outlook: What’s Next?
Advancements in smart membrane materials and AI-based monitoring are enhancing process control, reducing fouling, and enabling continuous bioprocessing. Membrane technology will continue to play a vital role in sustainable peptide production [3].
Conclusion
Membrane filtration remains a cornerstone in modern peptide purification, offering a unique blend of efficiency, scalability, and gentle handling. However, it requires a nuanced understanding of both process variables and material limitations to ensure consistent, bioactive, and cost-effective peptide outputs.
Looking for Membrane-Purified Peptides?
As a full-process manufacturer, PEPDOO® offers in-house ultrafiltration, membrane optimization, and QA-tested peptide ingredients for nutrition, beauty, and pharma applications. Contact us for custom solutions or samples today.
📩 Request a Custom QuoteFAQ
MWCOs between 1 kDa to 10 kDa are commonly used. Targeting specific bioactivities requires tight control of this range.
It is a non-thermal, gentle process that preserves peptide structure and function.
Often used as a primary purification method, it may be followed by chromatography for clinical applications.
Low-MW peptides may be lost or adsorbed. Process control is essential to minimize losses.
Ask about MWCOs, material compatibility, QA testing, and whether custom profiles are available.
Yes, it is widely used in industrial-scale peptide manufacturing.
Fouling reduces efficiency. Regular cleaning and anti-fouling membranes mitigate risks.
Yes. Manufacturers like PEPDOO® offer tailored membrane profiles for specific application needs.
References
- Sbroggio, M. F., Montilha, M. S., Figueiredo, V. R. G., et al. (2016). Functional properties of bovine collagen hydrolysate for food and pharmaceutical applications. Food Hydrocolloids, 61, 1–8.
- Cui, Y., Liu, Y., Wang, W., et al. (2020). Review on membrane fouling: Types, mechanisms and mitigation. Journal of Membrane Science, 605, 118118.
- Ma, Y., Zhang, Z., Zhang, Y., et al. (2023). Intelligent membrane separation systems for bio-manufacturing: A review. Separation and Purification Technology, 313, 123418.