The Power of Peptide Sequences: Precision Nutrition for Functional Health
In the fast-evolving world of functional nutrition and nutraceuticals, bioactive peptides are emerging as precision tools for enhancing human health. These short amino acid chains, derived from food proteins, are increasingly valued for their ability to deliver targeted physiological benefits—ranging from antioxidant support to blood pressure regulation. But what determines the function of a peptide? The answer lies in one critical factor: its amino acid sequence.
Understanding how sequence drives bioactivity enables ingredient manufacturers, supplement brands, and functional food developers to create more effective and scientifically-backed products. This article explores the central role amino acid sequences play in peptide function, with examples from collagen tripeptides, casein peptides, soy oligopeptides, and more.
The Structural Basis of Function
Peptides consist of amino acids joined by peptide bonds, usually comprising 2–50 residues. The linear sequence of these amino acids—known as the primary structure—is fundamental to the peptide’s function. This sequence dictates folding, receptor interactions, and biological targets [1].
For instance, the sequence Gly-Pro-Hyp (GPH) is the dominant component of collagen tripeptides, particularly those derived from fish skin. These tripeptides have been extensively studied for their ability to stimulate fibroblast activity and promote skin elasticity and joint support [2].
How Sequence Drives Bioactivity
Even peptides with the same molecular weight can behave differently based on sequence. The position of hydrophobic, polar, or charged residues affects a peptide’s ability to:
- Bind to enzymes or receptors
- Penetrate cell membranes
- Resist gastrointestinal degradation
Consider the well-known antihypertensive tripeptides Ile-Pro-Pro (IPP) and Val-Pro-Pro (VPP). These are the key bioactive fragments found in casein peptides, and their proline-rich sequences allow them to inhibit angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), helping to lower blood pressure [3].
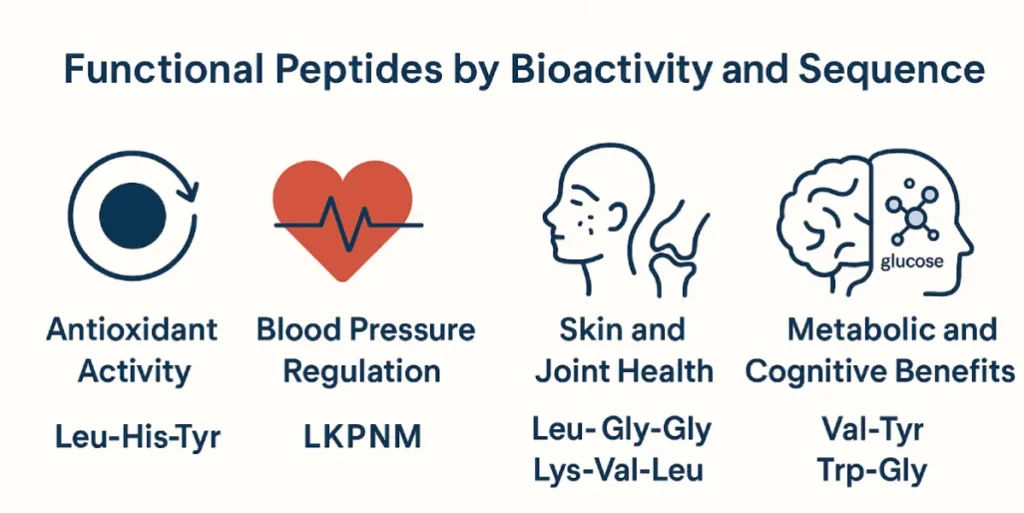
Functional Peptides by Bioactivity and Sequence
1. Antioxidant Activity
Antioxidant peptides typically contain residues such as tryptophan (Trp), tyrosine (Tyr), methionine (Met), and histidine (His). Examples include:
- Leu-His-Tyr (LHY) – from soy protein; key in soy oligopeptides [4]
- Cys-Gly-Tyr (CGY) – from egg white peptides
- Trp-Ala (WA) – from fish protein hydrolysates
2. Blood Pressure Regulation
Casein tripeptides, especially IPP and VPP, are known ACE inhibitors. Other examples include:
- Leu-Lys-Pro-Asn-Met (LKPNM) – from sardine muscle [5]
3. Skin and Joint Health
Peptides like Gly-Pro-Hyp, Pro-Hyp-Gly, and Ala-Hyp-Gly from collagen tripeptides stimulate collagen synthesis and promote dermal regeneration [2].
4. Immune Support
Short peptides from egg white proteins, such as Leu-Gly-Gly (LGG) and Lys-Val-Leu (KVL), enhance immune responses [6].
- Gln-Leu-Gln-Pro (QLQP) – from milk peptides
- Ala-Tyr-Gly (AYG) – from soy protein
5. Metabolic and Cognitive Benefits
Sequences like Val-Tyr (VY) and Trp-Gly (WG) can cross the blood-brain barrier and support glucose regulation and mood [7].
Enzymatic Hydrolysis: Unlocking Functional Sequences
Functional peptides are produced via enzymatic hydrolysis. For example:
- Gly-Pro-Hyp – from fish collagen via pepsin/collagenase
- LHY – from soy via alcalase [4]
- IPP, VPP – from casein via trypsin/chymotrypsin
Bioavailability and Transport
Peptides with sequences like Gly-Sar (GS), Val-Tyr (VY), and Met-Tyr (MY) are highly bioavailable due to their structure and use of PEPT1 transporters [8].
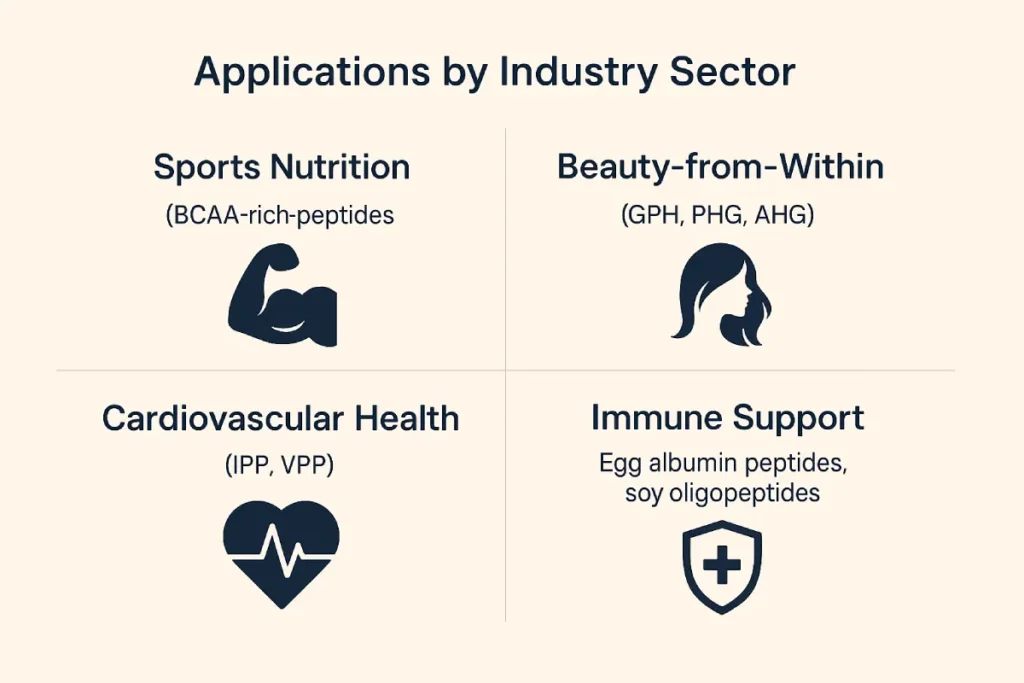
Applications by Industry Sector
- Sports Nutrition: BCAA-rich peptides like Leu-Leu-Val (LLV)
- Beauty-from-Within: Collagen tripeptides (GPH, PHG, AHG)
- Cardiovascular Health: Casein peptides (IPP, VPP)
- Immune Support: Egg albumin peptides, soy oligopeptides
Innovation: AI and Bioinformatics
Machine learning tools can predict peptide bioactivity based on sequence. Examples include predicted sequences like Tyr-Gly-Lys (YGK) and Ala-Gly-Lys-Arg (AGKR) now under validation [9].
Regulatory and IP Considerations
Certain peptides such as collagen tripeptides or casein peptides are patented. EU regulations may require novel food approval [10].
Conclusion
The amino acid sequence is the blueprint of peptide functionality. From collagen tripeptides to soy oligopeptides, understanding sequence-specific bioactivity is key to next-generation innovation in functional nutrition.
FAQ: Insights for Peptide Ingredient Buyers
The amino acid sequence is the specific order of amino acids that form a peptide chain. This sequence determines the peptide’s 3D structure and bioactivity. For example, the Gly-Pro-Hyp sequence in collagen tripeptides specifically stimulates skin collagen synthesis, enhancing elasticity and repair [1].
We provide a variety of high-purity peptide raw materials, including marine collagen tripeptides, casein peptides, and soy oligopeptides. All are produced using advanced enzymatic hydrolysis and nano-purification technologies to ensure high bioactivity and batch consistency.
Choose peptides with active sequences that align with your product goals. For beauty and skin health, collagen tripeptides are ideal; for immune support, soy oligopeptides are effective; for cardiovascular benefits, casein peptides containing IPP sequences are preferred.
Yes, all PEPDOO® peptides are backed by extensive clinical and in vitro studies to ensure safety and efficacy. The article references authoritative literature to help clients understand the scientific foundation.
This article helps you deeply understand peptide science, enabling your R&D to design more targeted and differentiated formulas. It also strengthens marketing with credible scientific backing, boosting consumer trust.
Yes, we have a professional R&D team and advanced manufacturing capabilities to customize peptides based on specific amino acid sequences, supporting innovative formula development and product upgrades.
Please contact our technical support team or submit an inquiry via our website. We provide detailed technical data, expert consultation, and sample support tailored to your needs.
References
- Korhonen, H., & Pihlanto, A. (2006). Bioactive peptides: Production and functionality. International Dairy Journal, 16(9), 945–960. Link
- Zague, V., et al. (2018). Collagen peptides modulate the metabolism of extracellular matrix by human dermal fibroblasts. Journal of Dermatological Treatment, 29(5). Link
- Nakamura, Y., et al. (1995). Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitors from sour milk. Journal of Dairy Science, 78(4), 777–783. Link
- Chen, H.-M., et al. (1995). Antioxidant activities of soybean peptides. J. Agric. Food Chem, 43(3), 574–578. Link
- Fujita, H., et al. (2001). Antihypertensive effect of casein hydrolysate. J. Human Hypertension, 15(7), 511–517. Link
- Mine, Y., & Kovacs-Nolan, J. (2006). Biologically active proteins and peptides from egg. World’s Poultry Science Journal, 62(1), 87–95. Link
- Hartmann, R., & Meisel, H. (2007). Food-derived peptides: From research to applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol, 18(2), 163–169. Link
- Vermeirssen, V., et al. (2004). Bioavailability of ACE inhibitory peptides. Br. J. Nutr, 92(3), 357–366. Link
- Wang, J., et al. (2019). AI-guided discovery of food-derived peptides. Trends Food Sci Technol, 89, 235–246. Link
- EUIPO. (2024). Patent and regulatory landscape of bioactive peptides. European Intellectual Property Office. Link