The Rise of Soy Peptides in Cardiometabolic Support: Clean-Label Solutions for B2B Brands
As the global burden of cardiometabolic diseases continues to rise, the functional nutrition industry is under increasing pressure to deliver evidence-based, clean-label solutions that support heart and metabolic wellness. Among the plant-based innovations gaining traction, soy peptides are emerging as a powerful ingredient category with scientifically supported benefits. Unlike conventional soy protein or isoflavones, soy peptides are bioactive fragments derived through enzymatic hydrolysis, specifically designed to target key markers in cardiometabolic health.
At PEPDOO®, a global source manufacturer of full-spectrum peptides, we specialize in developing clinically validated, plant-based ingredients like soy peptides to meet the evolving needs of B2B formulators and health brands. This article explores how soy peptides contribute to cardiometabolic support, the mechanisms behind their efficacy, and how brands can integrate them into next-generation formulations.
Understanding Cardiometabolic Health: A Global Challenge
Cardiometabolic health encompasses a range of interconnected conditions including hypertension, high cholesterol, insulin resistance, obesity, and chronic inflammation. These disorders are among the leading causes of death globally, contributing to heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. According to the World Health Organization, cardiovascular diseases claim an estimated 17.9 million lives annually [1].
The good news: functional nutrition has proven effective in mitigating risk factors when applied early and strategically. Key targets include:
- Lowering blood pressure
- Improving lipid profiles (LDL, HDL, total cholesterol)
- Enhancing glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity
- Reducing systemic inflammation and oxidative stress
What Are Soy Peptides?
Soy peptides are short-chain amino acid sequences obtained by enzymatically hydrolyzing soy protein isolates. Unlike intact proteins, these low-molecular-weight peptides (typically <1 kDa) are more bioavailable and can interact with specific physiological pathways related to cardiometabolic function [2].
Unlike soy isoflavones, which act through hormonal mechanisms, soy peptides act as bioactive modulators, binding to enzymes and receptors involved in vascular regulation, glucose metabolism, and fat oxidation. As a source manufacturer, PEPDOO® controls every stage of soy peptide production—from non-GMO soybean selection to enzyme-specific hydrolysis—ensuring consistent quality, bioactivity, and scalability.
Key attributes of soy peptides:
- Plant-based and vegan
- Easily absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract
- Heat- and pH-stable for various formulations
- Mild taste profile and excellent solubility
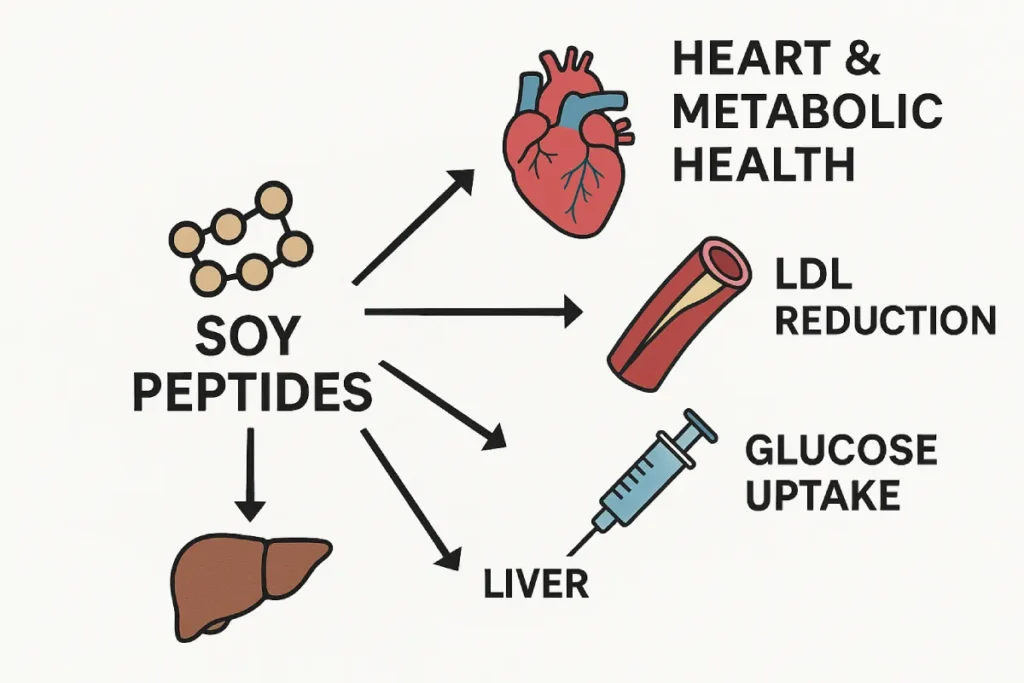
Mechanisms of Action in Cardiometabolic Support
1. Blood Pressure Regulation
One of the most studied effects of soy peptides is their ability to inhibit angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), which plays a key role in blood pressure control. Specific peptide sequences such as VHV, LSW, and YVV have been shown to reduce ACE activity, thereby promoting vasodilation and reducing blood pressure [3].
In a clinical study, subjects who consumed soy peptide-enriched supplements for 12 weeks experienced significant reductions in systolic and diastolic blood pressure compared to placebo [4].
2. Cholesterol and Lipid Metabolism
Soy peptides also exhibit hypolipidemic effects. Research indicates that they can downregulate genes responsible for hepatic cholesterol synthesis while enhancing LDL receptor activity in the liver [5]. Additionally, soy peptides may improve HDL levels and reduce triglyceride accumulation, supporting a balanced lipid profile.
3. Glucose Homeostasis and Insulin Sensitivity
Several peptides derived from soy have demonstrated the ability to enhance insulin signaling pathways. These peptides stimulate glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4) translocation and improve insulin receptor sensitivity, which may benefit individuals with insulin resistance or prediabetes [6].
Animal models have shown reduced fasting glucose and improved insulin response after soy peptide supplementation [7].
4. Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Activity
Chronic inflammation is both a cause and consequence of cardiometabolic disorders. Soy peptides can suppress the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6, while also reducing oxidative stress markers such as malondialdehyde (MDA) [8]. This dual action helps preserve vascular integrity and metabolic balance.
Scientific Validation and Clinical Data
Several human and animal studies support the efficacy of soy peptides in cardiometabolic applications:
- Blood pressure: A 2021 meta-analysis found that soy peptide supplementation led to a statistically significant reduction in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure across multiple trials [9].
- Lipid profile: Controlled studies show reductions in LDL-C by up to 10% over 8–12 weeks of supplementation [10].
- Glycemic control: Soy peptide interventions resulted in improved fasting glucose and HbA1c levels in overweight and prediabetic populations [11].
At PEPDOO®, we provide clinical summaries and technical dossiers to support regulatory submissions and product development.
Application Opportunities for B2B Brands
Soy peptides offer excellent formulation versatility across both supplement and food applications:
- Dietary supplements: Tablets, capsules, sachets, functional shots
- RTD beverages: Clear soy peptide solutions with enhanced bioavailability
- Functional foods: High-protein nutrition bars, plant-based yogurts, soups
- Synbiotic products: Combined with probiotics and fiber for metabolic synergy
Because soy peptides are highly soluble and neutral in taste, they can be easily incorporated without affecting product sensory qualities.
PEPDOO®‘s soy peptide solutions are optimized for easy integration into clean-label, vegan, and heart-health-focused product lines. Our peptides are manufactured in GMP-certified facilities and supported by full traceability, COA documentation, and formulation guidance.

Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Soy peptides are generally recognized as safe (GRAS) in the U.S. and widely accepted in global markets. However, soy remains a major allergen, and labeling must comply with regional regulations.
PEPDOO® supports B2B clients with:
- Export-ready documentation (COA, MSDS, HACCP, Halal, etc.)
- Non-GMO, allergen-declared production
- Support for novel food approval or blue-hat registration (China)
Our regulatory team works closely with clients to streamline compliance in international markets.
Why Partner with PEPDOO®?
As a global source manufacturer of full-spectrum peptides, PEPDOO® offers:
- Customized peptide production with enzyme-specific bioactivity targeting
- Both plant- and animal-derived peptides to meet diverse formulation needs
- Proprietary technologies for high-purity, high-bioavailability peptides
- Technical consultation and OEM/ODM support
- Full documentation for global registration and claims substantiation
Whether you’re developing heart-health supplements, metabolic beverages, or functional foods, PEPDOO® soy peptides offer a clinically validated, scalable, and clean-label solution.
Conclusion
With increasing demand for plant-based, science-driven solutions in the cardiometabolic category, soy peptides represent a compelling functional ingredient backed by both traditional use and modern science. Their multifunctional roles—from blood pressure and lipid regulation to glycemic control and anti-inflammatory effects—make them ideal for heart-health-focused formulations.
Partnering with a trusted manufacturer like PEPDOO® ensures not only ingredient quality but also expert support from R&D to commercialization. Soy peptides are more than a trend—they are a strategic opportunity for brands looking to lead in the future of functional nutrition.
📢 Ready to Develop Next-Generation Cardiometabolic Products?
PEPDOO® soy peptides are vegan, highly bioavailable, and clinically supported for heart and metabolic wellness.
🌱 Clean-label | 📄 Export-ready | 🧪 OEM/ODM Supported
👉 Contact Our B2B TeamFAQ
Soy peptides contain bioactive sequences such as lunasin, which can help reduce LDL cholesterol, improve insulin sensitivity, and regulate blood pressure by modulating key metabolic pathways [1]. These effects are backed by clinical and in vivo studies, making soy peptides a scientifically credible ingredient for heart and metabolic wellness products.
Soy peptides are short-chain amino acid fragments produced via enzymatic hydrolysis of soy protein. Unlike intact soy protein or isolated isoflavones, peptides are more bioavailable and can exhibit targeted physiological effects, including ACE inhibition, lipid metabolism regulation, and antioxidant activity. This gives formulators a more potent, precision-focused ingredient.
Yes. PEPDOO® soy peptides are plant-based, non-GMO, and free from artificial additives or animal derivatives, making them ideal for clean-label, vegan, and sustainable product development. We also offer traceability and batch documentation to support regulatory compliance and premium claims.
PEPDOO® offers soy peptide powders in various molecular weight distributions (<1kDa, 1–3kDa), suitable for:
- Functional beverages (RTDs)
- Sachets and powders
- Capsules and tablets
Custom formulation and granulation services are also available for turnkey product development.
Multiple studies have shown that soy-derived peptides reduce total cholesterol and triglycerides, lower systolic blood pressure, and improve glucose uptake by enhancing insulin signaling pathways [2][3]. PEPDOO® can provide published literature support and technical data upon request.
Absolutely. As a source manufacturer with full R&D capabilities, we provide OEM/ODM support including:
- Formula development tailored to your market
- Flavor optimization and sensory masking
- Peptide stability testing and shelf-life validation
We aim to be your long-term peptide innovation partner.
References
- World Health Organization. (2023). Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs).
- Hartmann, R., & Meisel, H. (2007). Food-derived peptides with biological activity: From research to food applications. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 18(2), 163–169.
- Li, G. H., Le, G. W., Shi, Y. H., & Shrestha, S. (2004). Angiotensin I–converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from food proteins and their physiological and pharmacological effects. Nutrition Research, 24(7), 469–486.
- Nakamura, Y., et al. (1995). Purification and characterization of angiotensin I–converting enzyme inhibitors from sour milk. Journal of Dairy Science, 78(4), 777–783.
- Cho, S. J., et al. (2007). Cholesterol-lowering mechanism of soybean protein hydrolysate in HepG2 cells. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 55(26), 10599–10604.
- Huang, W., et al. (2010). Lactic acid fermentation of rice improves the cholesterol-lowering activity of soy protein hydrolysate. Food Chemistry, 119(2), 553–558.
- Kwon, D. Y., et al. (2006). Soy peptide supplementation improves lipid and glucose metabolism in aged mice. Nutrition Research, 26(12), 578–584.
- Zhang, J., & Wang, Y. (2020). Anti-inflammatory and antioxidative effects of soybean peptides in LPS-induced macrophages. Journal of Functional Foods, 68, 103893.
- Kim, H., & Kim, J. (2021). Soy peptide supplementation and blood pressure: A meta-analysis. Nutrition Reviews, 79(8), 838–849.
- Acharjee, S., & Ghosh, A. (2014). Evaluation of cholesterol-lowering activity of soy peptide fractions in human subjects. International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition, 65(6), 719–725.
- Lin, Y., & Liu, C. (2022). Effects of soy peptides on glycemic control: A randomized clinical trial. Journal of Functional Foods, 88, 104902.