A Tale of Two Proteins: Whey and Casein Peptides in Focus
In the evolving landscape of functional nutrition, protein-derived peptides have emerged as high-impact bioactive ingredients. Among the most commercially valuable are whey peptides and casein peptides, each offering distinct functionalities for product developers targeting sports nutrition, weight management, cardiovascular support, and more.
This article explores the origins, bioactive differences, and practical applications of these two milk-derived peptide types—helping formulators, brand managers, and ingredient buyers make informed decisions for their next-generation functional product.
Origins and Production Methods
Whey peptides and casein peptides originate from cow’s milk, yet they stem from different fractions. Whey makes up about 20% of milk protein and is the liquid byproduct of cheese production, while casein accounts for roughly 80% and forms the curd.
Both peptide types are typically produced through enzymatic hydrolysis, breaking down the intact proteins into smaller, more bioavailable chains of amino acids—mainly dipeptides and tripeptides [1]. This process not only enhances absorption but also activates a range of biological functions, from anti-inflammatory to antihypertensive effects.
Nutritional & Bioactive Composition
Amino Acid Profile
Whey peptides are rich in branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs)—especially leucine—making them ideal for muscle protein synthesis and athletic recovery [2]. On the other hand, casein peptides contain higher levels of glutamine and proline, supporting gut health, stress resilience, and tissue repair.
Bioactivity Spectrum
- Whey Peptides: Antioxidant, antimicrobial, and ACE-inhibitory functions; rapid absorption and immune modulation
- Casein Peptides: Opioid-like peptides for satiety, blood pressure regulation (via IPP, VPP), and gut microbiota modulation [3]
Absorption and Bioavailability
Whey peptides are fast-acting, entering the bloodstream quickly and triggering immediate physiological responses—particularly beneficial in sports nutrition. In contrast, casein peptides are digested more slowly, offering a sustained release of amino acids and a more prolonged functional impact [4].
Functional Benefits in Key Health Areas
Sports Nutrition & Muscle Recovery
Whey peptides are considered the gold standard for post-exercise recovery, thanks to their rapid digestibility and leucine-rich profile that stimulates muscle protein synthesis (MPS) [5]. Casein peptides, however, shine in night-time recovery formulations, maintaining a steady supply of amino acids and reducing muscle breakdown during sleep.
Weight Management and Satiety
Casein peptides exhibit appetite-suppressing properties, partially due to casomorphins—bioactive peptides with mild opioid activity that delay gastric emptying and promote fullness [6]. Whey peptides, by contrast, may support thermogenesis and fat oxidation, making them suitable for daytime weight management products.
Cardiovascular Health
Casein-derived tripeptides such as IPP (Ile-Pro-Pro) and VPP (Val-Pro-Pro) have shown significant ACE-inhibitory effects, helping regulate blood pressure in hypertensive individuals [7]. Whey peptides also contribute to cardiovascular support through nitric oxide-mediated vasodilation and anti-inflammatory activity.
Immune and Gut Support
Certain peptides in whey—such as lactoferricin—possess antimicrobial and immune-enhancing properties [8]. Meanwhile, casein peptides may act as prebiotics, modulating beneficial gut bacteria and enhancing intestinal barrier integrity—an emerging area of interest for gut-targeted functional foods.
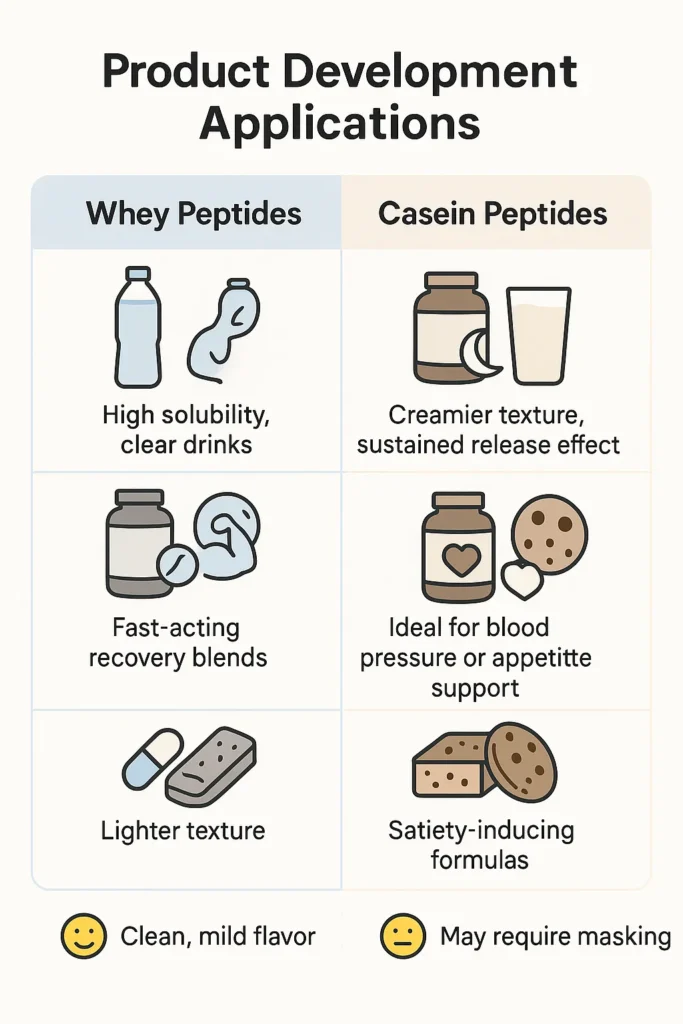
Product Development Applications
Both peptide types are highly versatile, but formulation decisions depend on the product format and target health outcome.
| Product Format | Whey Peptides | Casein Peptides |
|---|---|---|
| RTD Beverages | High solubility, clear drinks | Creamier texture, sustained release effect |
| Protein Powders | Fast-acting recovery blends | Nighttime or meal-replacement applications |
| Capsules/Tablets | Easy delivery of bioactive dose | Ideal for blood pressure or appetite support |
| Bars and Snacks | Lighter texture | Satiety-inducing formulas |
Taste is another key factor—whey peptides tend to have a cleaner flavor, while casein peptides may require masking in consumer-ready products.
Regulatory and Labeling Considerations
Both ingredients are recognized as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) in the U.S. and approved by EFSA in Europe. However, product developers should:
- Clearly declare allergen information for dairy-derived peptides
- Ensure halal, kosher, or clean-label claims if relevant to market strategy
- Check local regulatory limits for peptide-specific health claims
Formulation Insights for R&D Teams
When choosing between whey and casein peptides, R&D teams must evaluate:
- Solubility and stability: Whey peptides are more soluble and stable in acidic beverages
- Cost-efficiency: Whey peptides may be more cost-effective due to broader availability
- Synergistic potential: Blending both peptides can deliver fast and sustained release
- Heat and pH tolerance: Important for baked goods and shelf-stable RTDs
Market Trends & Consumer Insights
The “protein plus” trend—where consumers demand protein with added functionality—is driving the growth of peptide-based ingredients. According to recent surveys:
- 65% of active consumers recognize whey protein as beneficial for fitness and recovery [9]
- Casein peptides are gaining traction in sleep, satiety, and cardiovascular product categories
- Clean-label, non-GMO, and sustainably sourced peptides are increasingly prioritized
Summary: Which Is Better for Your Functional Product?
| Criteria | Whey Peptides | Casein Peptides |
|---|---|---|
| Digestion Speed | Fast-absorbing | Slow-releasing |
| Best Use Case | Muscle recovery, performance | Satiety, cardiovascular, gut health |
| Flavor Profile | Cleaner, less bitter | Creamier, may need masking |
| Ideal Formats | RTDs, sachets, post-workout powders | Nighttime blends, satiety bars, tablets |
| Regulatory Clarity | Widely accepted | Same, but niche claims growing |
| Shelf Life and Stability | Stable in liquids | Stable in dry formats |
Verdict: If you’re developing a sports or performance product, whey peptides are likely your go-to. For weight management, cardiovascular, or gut health, casein peptides offer unique advantages. A hybrid approach may provide the best of both worlds.
FAQ
Yes. Combining them provides both fast and sustained peptide activity, ideal for 24-hour formulations.
Most hydrolyzed peptides are virtually lactose-free, but it’s essential to verify with suppliers.
Hydrolysates may include larger fragments; peptides refer to short-chain amino acids with proven bioactivity.
Casein peptides, due to their slower absorption and casomorphin-related satiety effects.
Yes. Whey peptides are generally cleaner; casein peptides may need flavor masking strategies.
References
- Korhonen, H., & Pihlanto, A. (2006). Bioactive peptides: Production and functionality. International Dairy Journal, 16(9), 945–960.
- Tipton, K. D., & Wolfe, R. R. (2004). Protein and amino acids for athletes. Journal of Sports Sciences, 22(1), 65–79.
- FitzGerald, R. J., & Meisel, H. (2003). Milk protein-derived peptide inhibitors of ACE. British Journal of Nutrition, 89(S1), S3–S10.
- Boirie, Y., et al. (1997). Slow and fast dietary proteins differently modulate postprandial protein accretion. PNAS, 94(26), 14930–14935.
- Tang, J. E., et al. (2009). Different muscle protein anabolic responses to whey, casein, and soy. Journal of Applied Physiology, 107(3), 987–992.
- Phelan, M., et al. (2009). Review: Bioactivities of caseinophosphopeptides. International Dairy Journal, 19(10), 643–651.
- Seppo, L., et al. (2003). Milk peptides and blood pressure: A meta-analysis. Nutrition Journal, 2(1), 1–6.
- Legrand, D. (2016). Lactoferrin and immune processes. Biochemistry and Cell Biology, 94(1), 1–9.
- FMCG Gurus. (2024). Sports Nutrition Global Survey Report.