Choosing the Right Recovery Ingredient: Whey Peptides or Whey Protein?
As the sports nutrition market continues to expand, product differentiation and scientific validation are becoming non-negotiable for brands and formulators. Among the most debated topics today is whether whey peptides outperform traditional whey protein when it comes to post-workout recovery.
While both originate from the same dairy source, their structural differences translate into distinct physiological impacts. In this article, we explore the science, absorption profiles, and formulation value of whey peptides vs whey protein to help you make an informed decision for your next-generation recovery product.
Understanding the Basics
What is Whey Protein?
Whey protein is derived from the liquid byproduct of cheese production. It contains a mix of intact proteins, rich in essential amino acids—especially branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) like leucine. Available in forms such as concentrate (WPC), isolate (WPI), and hydrolysate (WPH), whey protein has long been the go-to ingredient in fitness powders, bars, and beverages.
What are Whey Peptides?
Whey peptides are short chains of amino acids, typically di- and tri-peptides, derived from enzymatically hydrolyzing whey protein. These small peptides are more than just partially digested proteins—they represent a bioavailable, fast-acting, and functionally enhanced form of nutrition. Their solubility, rapid absorption, and potential bioactivities make them particularly attractive in performance recovery and clinical formulations.
As a full-process whey peptide manufacturer, PEPDOO® produces formulation-ready peptides through proprietary enzymatic hydrolysis, delivering molecularly consistent, low-allergen, and rapidly absorbed peptides trusted by global brands.
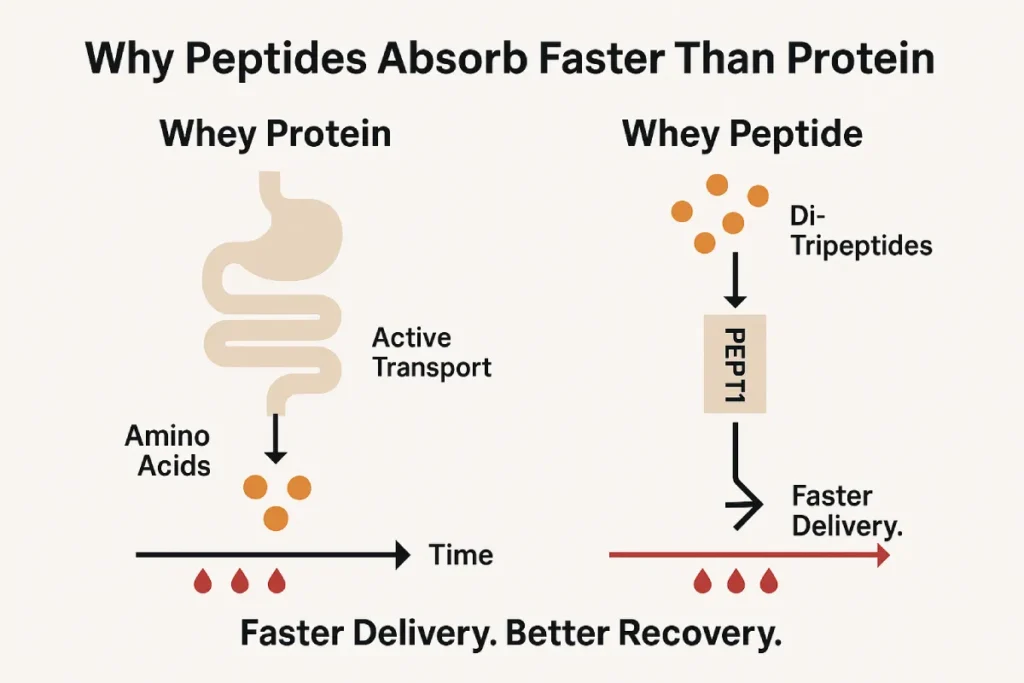
Absorption and Bioavailability: A Key Advantage
Faster Uptake Through Peptide Transporters
Unlike intact proteins, which must undergo breakdown into free amino acids before absorption, di- and tri-peptides are absorbed directly via specialized transporters like PEPT1 in the intestinal wall [1]. This allows peptides to bypass certain metabolic delays, resulting in faster plasma amino acid elevations post-ingestion.
Bioavailability and Peak Amino Acid Levels
Clinical studies have shown that whey peptides lead to faster and higher peak plasma leucine levels compared to standard whey isolate [2]. Since leucine is a critical activator of the mTOR pathway—responsible for muscle protein synthesis (MPS)—this can have meaningful implications for muscle repair and growth.
PEPDOO® supports partners with absorption kinetics data and customized peptide profiles to optimize the recovery window (30–60 minutes post-exercise).
Muscle Recovery and Performance Benefits
Enhanced Muscle Protein Synthesis (MPS)
Rapid delivery of amino acids to muscle tissue post-exercise enhances MPS and reduces muscle breakdown. Studies comparing peptide vs whole protein supplementation found that peptides led to more rapid MPS stimulation, especially in the immediate post-workout phase [3].
Reducing Muscle Soreness and Inflammation
Some peptides exhibit anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, helping reduce DOMS (delayed onset muscle soreness). Specific peptide sequences have been shown to lower markers of oxidative stress and inflammation—beneficial for athletes in high-frequency training cycles [4].
Supporting Glycogen Replenishment
Peptides may also play a role in co-transport with glucose, accelerating glycogen resynthesis. Peptides like Gly-Gln have been explored for their role in improving post-exercise nutrient uptake and intestinal recovery [5].
Scientific Evidence: Peptides in Focus
Recent research has highlighted several advantages of whey peptides:
- Faster gastric emptying and intestinal absorption compared to WPI [2].
- Higher MPS rates when consumed immediately post-exercise [3].
- Improved recovery markers such as reduced CK and LDH in blood [4].
PEPDOO® provides preclinical validation, peptide fingerprinting, and functional activity testing for brands seeking to substantiate recovery claims.
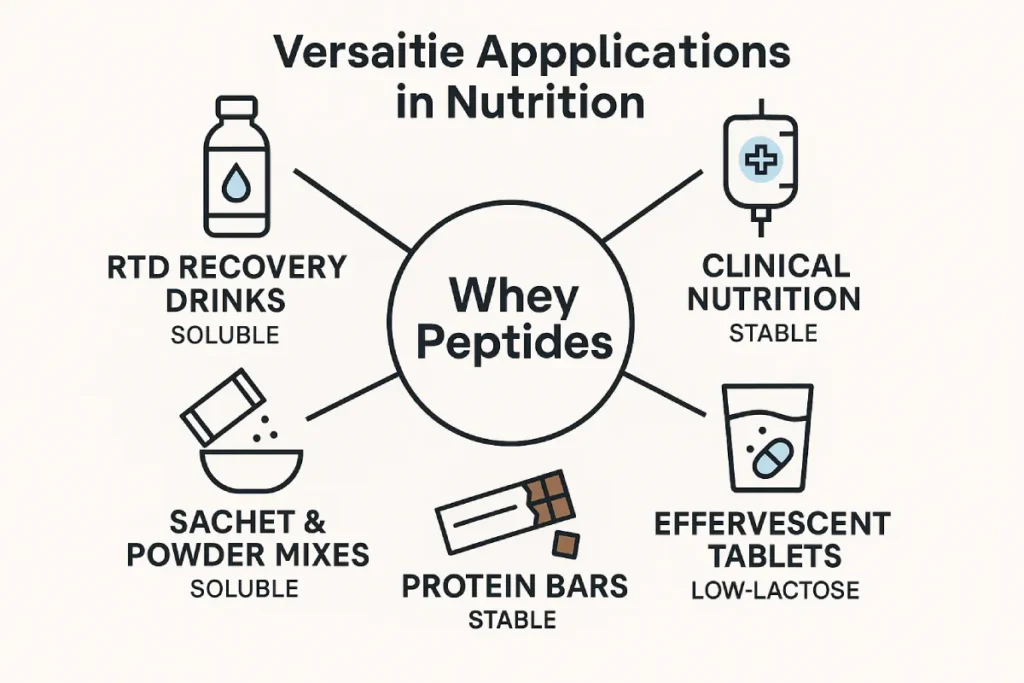
Formulation Considerations
Clean-Label, Functional, and Versatile
Whey peptides offer excellent solubility, neutral flavor, and fast dispersion, making them suitable for:
- RTD beverages
- High-protein sachets
- Functional shots
- Effervescent tablets
- Clinical recovery formulas
As a source manufacturer, PEPDOO® offers batch-customized peptides (200–1000 Da), free-flowing powder, and lactose-free specifications to meet your target application.
Which is Better for Recovery?
If your formulation goal is rapid recovery, enhanced bioavailability, and high consumer performance satisfaction, whey peptides offer a decisive edge. However, for cost-sensitive mass-market products, whey protein still serves as a reliable backbone.
| Parameter | Whey Protein | Whey Peptides |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Size | 10–50 kDa | <1 kDa |
| Absorption Speed | Moderate | Fast |
| Solubility | Good | Excellent |
| Functional Activity | Low | High (bioactive potential) |
| Ideal Use | General fitness | Elite athletes, clinical, fast recovery |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Whether you’re launching a next-gen sports nutrition line or upgrading an existing formula, PEPDOO® supports full-chain solutions from hydrolysis to finished product integration.
Conclusion
Whey peptides and whey protein each serve valuable roles in the recovery nutrition landscape. However, for brands prioritizing efficacy, speed, and scientific edge, peptides are the clear winner.
PEPDOO® empowers global formulators with clinically relevant whey peptides, optimized for absorption, solubility, and functional performance. With over 6,000 MT annual peptide capacity, in-house QA, and export-ready documentation, we serve as your trusted peptide partner from source to solution.
📩 Ready to Upgrade Your Recovery Formula?
Partner with PEPDOO® to access fully traceable, enzyme‑hydrolyzed whey peptides with verified stability, targeted molecular weights, and clean‑label compliance.
FAQ
Whey peptides are short chains of amino acids produced through enzymatic hydrolysis of whey protein. This pre-digestion step enhances their bioavailability and allows faster absorption through peptide transporters (PepT1), unlike intact proteins that must be fully broken down into free amino acids.
✅ B2B Insight: For formulators, this means better nutrient delivery in time-sensitive applications like post-workout RTDs or clinical nutrition.
Studies show that di- and tri-peptides are absorbed more rapidly than free amino acids due to active transport via peptide carriers in the small intestine [1]. At PEPDOO®, we provide in vitro transport models and peptide absorption curves to help R&D teams validate functionality.
📊 Data available: Peptide transport rate, plasma amino acid kinetics, molecular weight distribution.
es, especially when processed under controlled enzymatic conditions. At PEPDOO®, our whey peptides are tested for thermal stability, pH tolerance (3.5–7.5), and long-term storage behavior. We also offer encapsulation or flavor masking solutions if needed.
🔬 Available support: Shelf-life stability reports, accelerated aging data, compatibility with minerals or botanicals.
Absolutely. We offer custom molecular weight ranges (e.g., <1000 Da, <500 Da) to match desired bioactivity profiles—whether your goal is fast recovery, immune support, or anabolic response.
🎯 Custom solutions: Defined peptide cuts, low bitterness, neutral taste, formulation-ready.
Yes. Our whey peptides are:
Lactose-free and allergen-controlled
Manufactured under GMP and ISO22000
Export-ready with documentation for FDA, EFSA, CFDA, Halal, and Kosher
📑 B2B Assurance: Full COA, SDS, spec sheets, and regulatory dossiers provided.
Whey peptides are suitable for:
RTD beverages (clear or flavored)
Stick pack powders and sachets
Effervescent tablets
Clinical nutrition applications
Nutraceutical gummies or capsules
🧪 Ask us about solubility, pH clarity, flavor interaction, and delivery systems.
Yes. We offer:
Custom sampling and bench-scale trials
Joint R&D for functionality claims
Stability, flavor, and application testing
Regulatory documentation and compliance support
🤝 One-stop peptide partner from molecule design to final application.
References
[1] Matthews, D. E. (2020). Peptide transport and absorption: PEPT1 and beyond. Annual Review of Nutrition, 40(1), 391–412.
[2] Koopman, R., et al. (2009). Ingestion of whey hydrolysate, casein, or soy protein isolate: Effects on muscle protein synthesis. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 90(1), 131–139.
[3] Pasiakos, S. M., et al. (2015). Leucine-enriched whey protein ingestion improves muscle protein synthesis and recovery after exercise. Nutrition & Metabolism, 12, 1–8.
[4] Morifuji, M., et al. (2010). Dietary whey protein increases liver and skeletal muscle glutathione content and improves endurance performance in rats. Nutrition, 26(3), 255–261.
[5] van Loon, L. J., et al. (2000). Plasma insulin responses after ingestion of different amino acid or protein mixtures with carbohydrate. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 72(1), 96–105.